 “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid derived from Cannabis sativa. CBD initially drew scientific interest due to its anticonvulsant properties but increasing evidence of other therapeutic effects has attracted the attention of additional clinical and non-clinical populations, including athletes.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid derived from Cannabis sativa. CBD initially drew scientific interest due to its anticonvulsant properties but increasing evidence of other therapeutic effects has attracted the attention of additional clinical and non-clinical populations, including athletes.
Unlike the intoxicating cannabinoid, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), CBD is no longer prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency and appears to be safe and well-tolerated in humans. It has also become readily available in many countries with the introduction of over-the-counter “nutraceutical” products.
The aim of this narrative review was to explore various physiological and psychological effects of CBD that may be relevant to the sport and/or exercise context and to identify key areas for future research. As direct studies of CBD and sports performance are is currently lacking, evidence for this narrative review was sourced from preclinical studies and a limited number of clinical trials in non-athlete populations.
Preclinical studies have observed robust anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective and analgesic effects of CBD in animal models. Preliminary preclinical evidence also suggests that CBD may protect against gastrointestinal damage associated with inflammation and promote healing of traumatic skeletal injuries. However, further research is required to confirm these observations.
Early stage clinical studies suggest that CBD may be anxiolytic in “stress-inducing” situations and in individuals with anxiety disorders. While some case reports indicate that CBD improves sleep, robust evidence is currently lacking. Cognitive function and thermoregulation appear to be unaffected by CBD while effects on food intake, metabolic function, cardiovascular function, and infection require further study.
CBD may exert a number of physiological, biochemical, and psychological effects with the potential to benefit athletes. However, well controlled, studies in athlete populations are required before definitive conclusions can be reached regarding the utility of CBD in supporting athletic performance.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32632671/
“CBD has been reported to exert a number of physiological, biochemical, and psychological effects that have the potential to benefit athletes. For instance, there is preliminary supportive evidence for anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, analgesic, and anxiolytic actions of CBD and the possibility it may protect against GI damage associated with inflammation and promote the healing of traumatic skeletal injuries.”
https://sportsmedicine-open.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40798-020-00251-0
 “Phytocannabinoids are bioactive natural products found in some flowering plants, liverworts, and fungi that can be beneficial for the treatment of human ailments such as pain, anxiety, and cachexia. Targeted biosynthesis of cannabinoids with desirable properties requires identification of the underlying genes and their expression in a suitable heterologous host. We provide an overview of the structural classification of phytocannabinoids based on their decorated resorcinol core and the bioactivities of naturally occurring cannabinoids, and we review current knowledge of phytocannabinoid biosynthesis in Cannabis, Rhododendron, and Radula species. We also highlight the potential in planta roles of phytocannabinoids and the opportunity for synthetic biology approaches based on combinatorial biochemistry and protein engineering to produce cannabinoid derivatives with improved properties.”
“Phytocannabinoids are bioactive natural products found in some flowering plants, liverworts, and fungi that can be beneficial for the treatment of human ailments such as pain, anxiety, and cachexia. Targeted biosynthesis of cannabinoids with desirable properties requires identification of the underlying genes and their expression in a suitable heterologous host. We provide an overview of the structural classification of phytocannabinoids based on their decorated resorcinol core and the bioactivities of naturally occurring cannabinoids, and we review current knowledge of phytocannabinoid biosynthesis in Cannabis, Rhododendron, and Radula species. We also highlight the potential in planta roles of phytocannabinoids and the opportunity for synthetic biology approaches based on combinatorial biochemistry and protein engineering to produce cannabinoid derivatives with improved properties.”
 “Deposition of amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptide in the brain is the leading source of the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Recent studies have suggested that anti-amyloidogenic agents may be a suitable therapeutic strategy for AD.
“Deposition of amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptide in the brain is the leading source of the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Recent studies have suggested that anti-amyloidogenic agents may be a suitable therapeutic strategy for AD. “Cannabinoids may have an important therapeutic potential for the treatment of dependence on crack cocaine.
“Cannabinoids may have an important therapeutic potential for the treatment of dependence on crack cocaine.

 “Like most modern molecular biology and natural product chemistry, understanding cannabinoid pharmacology centers around molecular interactions, in this case, between the cannabinoids and their putative targets, the G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). Understanding the complex structure and interplay between the partners in this molecular dance is required to understand the mechanism of action of synthetic, endogenous, and phytochemical cannabinoids. This review, with 91 references, surveys our understanding of the structural biology of the cannabinoids and their target receptors including both a critical comparison of the extant crystal structures and the computationally derived homology models, as well as an in-depth discussion about the binding modes of the major cannabinoids. The aim is to assist in situating structural biochemists, synthetic chemists, and molecular biologists who are new to the field of cannabis research.”
“Like most modern molecular biology and natural product chemistry, understanding cannabinoid pharmacology centers around molecular interactions, in this case, between the cannabinoids and their putative targets, the G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). Understanding the complex structure and interplay between the partners in this molecular dance is required to understand the mechanism of action of synthetic, endogenous, and phytochemical cannabinoids. This review, with 91 references, surveys our understanding of the structural biology of the cannabinoids and their target receptors including both a critical comparison of the extant crystal structures and the computationally derived homology models, as well as an in-depth discussion about the binding modes of the major cannabinoids. The aim is to assist in situating structural biochemists, synthetic chemists, and molecular biologists who are new to the field of cannabis research.” “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid derived from Cannabis sativa. CBD initially drew scientific interest due to its anticonvulsant properties but increasing evidence of other therapeutic effects has attracted the attention of additional clinical and non-clinical populations, including athletes.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid derived from Cannabis sativa. CBD initially drew scientific interest due to its anticonvulsant properties but increasing evidence of other therapeutic effects has attracted the attention of additional clinical and non-clinical populations, including athletes. “Objectives: To investigate the action of cannabinoids on spasticity and pain in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis, by means of neurophysiological indexes.
“Objectives: To investigate the action of cannabinoids on spasticity and pain in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis, by means of neurophysiological indexes. “Astrocytomas, the most prevalent primary brain tumors, can be divided by histology and malignancy levels into four following types: pilocytic astrocytoma (grade I), diffuse fibrillary astrocytoma (grade II), anaplastic astrocytoma (grade III), and glioblastoma multiforme (grade IV). For high grade astrocytomas (grade III and grade IV), blood vessels formation is considered as the most important property.
“Astrocytomas, the most prevalent primary brain tumors, can be divided by histology and malignancy levels into four following types: pilocytic astrocytoma (grade I), diffuse fibrillary astrocytoma (grade II), anaplastic astrocytoma (grade III), and glioblastoma multiforme (grade IV). For high grade astrocytomas (grade III and grade IV), blood vessels formation is considered as the most important property. “Hempseeds, the edible fruits of the Cannabis sativa L. plant, were initially considered a by-product of the hemp technical fibre industry. Nowadays, following the restorationing of the cultivation of C. sativa L. plants containing an amount of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) <0.3% or 0.2% (industrial hemp) there is a growing interest for the hempseeds production due to their high nutritional value and functional features.
“Hempseeds, the edible fruits of the Cannabis sativa L. plant, were initially considered a by-product of the hemp technical fibre industry. Nowadays, following the restorationing of the cultivation of C. sativa L. plants containing an amount of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) <0.3% or 0.2% (industrial hemp) there is a growing interest for the hempseeds production due to their high nutritional value and functional features.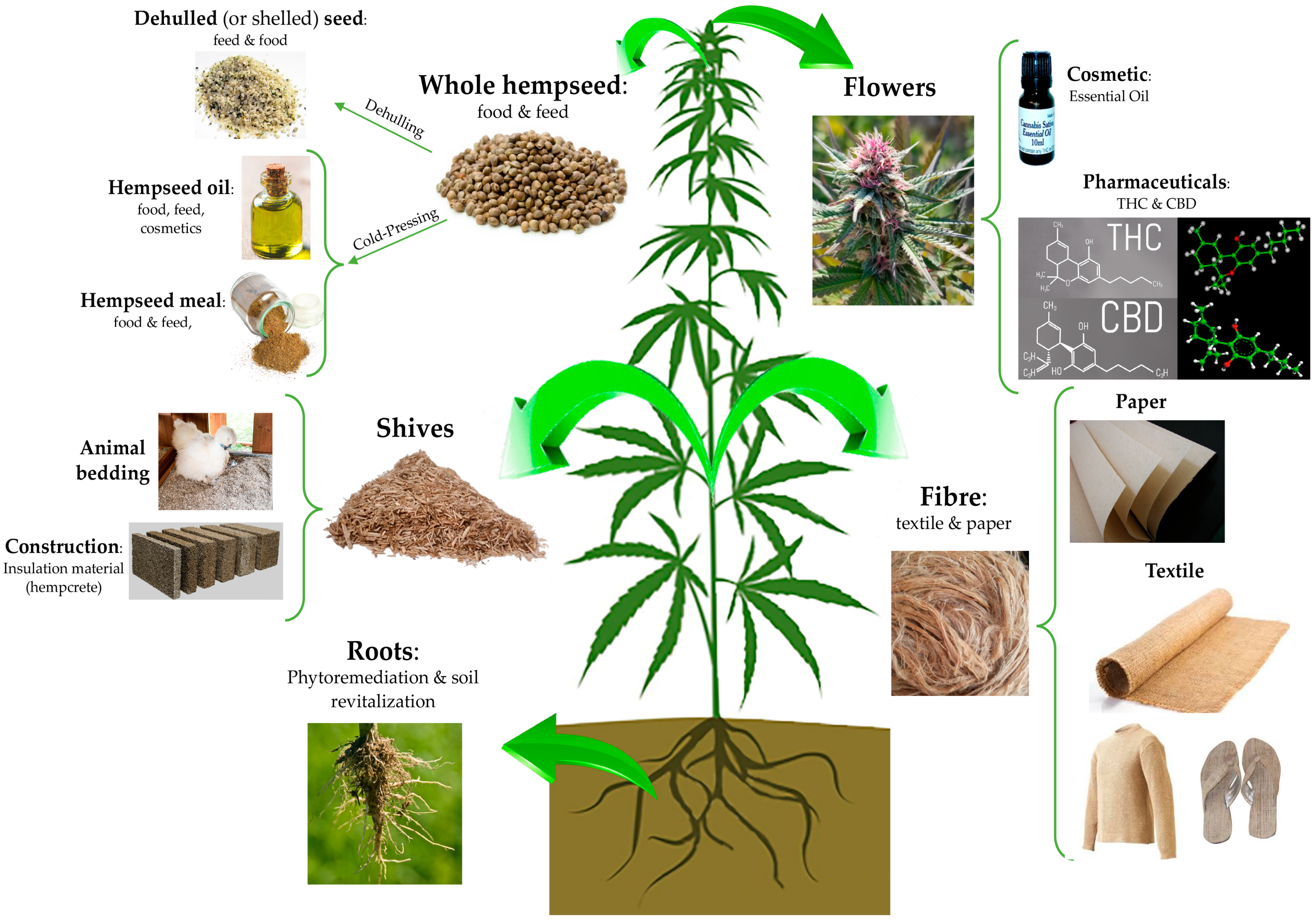
 “Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening complication that can ensue following Staphylococcus aureus infection. The enterotoxin produced by these bacteria (SEB) acts as a superantigen thereby activating a large proportion of T cells leading to cytokine storm and severe lung injury.
“Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening complication that can ensue following Staphylococcus aureus infection. The enterotoxin produced by these bacteria (SEB) acts as a superantigen thereby activating a large proportion of T cells leading to cytokine storm and severe lung injury.