 “Abusive alcohol consumption is a health problem, worldwide.
“Abusive alcohol consumption is a health problem, worldwide.
There is extensive literature indicating that cannabinoid 1 receptor (CB1R) plays a crucial role in mediating alcohol’s reward effects.
Maternal care deprivation (MCD) is a reliable rodent model of early life stress that leads to high levels of anxiety and alterations in motivation, which may increase vulnerability to alcohol consumption.
The present study researched whether anxiety-like behaviors and the level of motivation for a natural reward, and CB1R expression in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and nucleus accumbens (NAcc) can predict alcohol consumption in non-MCD and MCD male rats.
Results indicate that MCD increases anxiety-like behaviors, i.e., reduces time in open arms in the elevated plus maze and increases alcohol intake. In turn, the motivation for a palatable reward, i.e., a chocolate flavored pellet, was not affected by MCD.
MCD reduces CB1R expression in the PFC and increases it in the NAcc. Hence, both higher anxiety-like behaviors and higher CB1R expression in the NAcc and lower CB1R expression in the PFC are associated with higher alcohol intake.
These results suggest that early life adverse experiences induce a reprogramming of the brain’s endocannabinoid system that very likely contributes to making the brain vulnerable to develop alcohol abuse and dependence.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31568767
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006899319305396?via%3Dihub


 “Use of medical cannabis for improving symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease is increasing. However, reports on long-term outcomes are lacking. This prospective, observational study assessed the effects of licensed cannabis use among patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
“Use of medical cannabis for improving symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease is increasing. However, reports on long-term outcomes are lacking. This prospective, observational study assessed the effects of licensed cannabis use among patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
 “Muscle pain affects approximately 11-24% of the global population.
“Muscle pain affects approximately 11-24% of the global population. “Indisputably, cancer is a global crisis that requires immediate intervention. Despite the use of conventional treatments over the past decades, it is acceptable to admit that these are expensive, invasive, associated with many side effects and, therefore, a reduced quality of life.
“Indisputably, cancer is a global crisis that requires immediate intervention. Despite the use of conventional treatments over the past decades, it is acceptable to admit that these are expensive, invasive, associated with many side effects and, therefore, a reduced quality of life.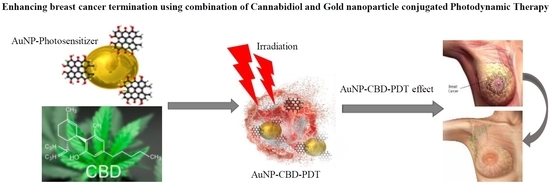

 “Here, we hypothesized that adolescent Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) worsens the impact of prenatal maternal immune activation (MIA) on ventral tegmental area (VTA) dopamine cells in rat offspring.
“Here, we hypothesized that adolescent Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) worsens the impact of prenatal maternal immune activation (MIA) on ventral tegmental area (VTA) dopamine cells in rat offspring. “Cannabinoid receptors have been detected in human gliomas and cannabinoids have been proposed as novel drug candidates in the treatment of brain tumors.
“Cannabinoid receptors have been detected in human gliomas and cannabinoids have been proposed as novel drug candidates in the treatment of brain tumors. “Substance use disorder (SUD) is a major public health crisis worldwide, and effective treatment options are limited.
“Substance use disorder (SUD) is a major public health crisis worldwide, and effective treatment options are limited.