 “Cannabis sativa is a well-known plant which has been of benefit since ancient times in several medicinal systems, including Chinese, Indian, Greek and Egyptian ones.
“Cannabis sativa is a well-known plant which has been of benefit since ancient times in several medicinal systems, including Chinese, Indian, Greek and Egyptian ones.
Although C. sativa is one of the most investigated medicinal plants in the world, it faces the most controversial of issues for its legalization as a medication. C. sativa contains several hundreds of phytoconstituents including the infamous «cannabinoid.” It is necessary to properly understand the medicinal importance of these phytochemicals and spread awareness among the countries where it’s still facing legal complexities.
The current review is focusing on most recent literature pertaining to the various applications of cannabinoids with a special focus on medicinal aspect of the phytochemicals. Peer reviewed articles focusing on the importance of cannabis and cannabinoids were the target of this review. Articles were selected based on the relevance to the general scope of the work i.e. application of cannabinoids.
Cannabinoids can truly be regarded as wonder drug keeping their immense diversity of usage but unfortunately, many of the mares never researched biologically or pharmacologically due to their low yield in the plant. However, the approval of some cannabinoids by the FDA (along with other recognized national medical health systems) has opened the horizons for the explicit use of these natural drugs in medicines such as Epidiolex® (cannabidiol used for the treatment of severe forms of epilepsy) and Sativex®(‘Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol’ used for the treatment of spasticity caused by multiple sclerosis, aka: MS.)
Many pharmacological properties of C. sativa are attributed to cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive component, along with Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9 -THC), a psychoactive component. This review addresses the most important application or current utilization of cannabinoids in a variety of treatments such as: chronic pain, cancer, emesis, anorexia, irritable bowel syndrome, communicative diseases, glaucoma and central nervous system disorders. The biosynthetic pathway of cannabinoids is also discussed. In short, this plant has a myriad of bioactive compounds which have the potential to increase the list of approved cannabinoids suitable for therapy.”

 “In the last decade the use of medical cannabis (MC) for palliative cancer treatment has risen. However, the choice between products is arbitrary and most patients are using Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-dominant cannabis products.
“In the last decade the use of medical cannabis (MC) for palliative cancer treatment has risen. However, the choice between products is arbitrary and most patients are using Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-dominant cannabis products. “Cannabis is increasingly being used for medicinal purposes but remains outside Western medical practice. Data on perioperative use and outcomes are scarce. Few surgeons receive training regarding legal endorsement, reported medicinal benefits, and potential risks, making it difficult to advise patients. Guidelines and additional research are needed.
“Cannabis is increasingly being used for medicinal purposes but remains outside Western medical practice. Data on perioperative use and outcomes are scarce. Few surgeons receive training regarding legal endorsement, reported medicinal benefits, and potential risks, making it difficult to advise patients. Guidelines and additional research are needed. “UV radiation is a well-established environmental risk factor known to cause oxidative stress and disrupt the metabolism of keratinocyte phospholipids. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
“UV radiation is a well-established environmental risk factor known to cause oxidative stress and disrupt the metabolism of keratinocyte phospholipids. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.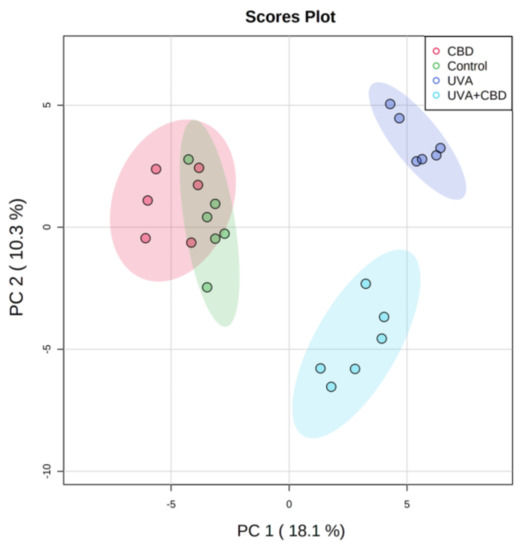
 “Leukocytes are part of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and are critical determinants of tumor progression. Because of the immunoregulatory properties of cannabinoids, the endocannabinoid system (ECS) may have an important role in shaping the TME.
“Leukocytes are part of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and are critical determinants of tumor progression. Because of the immunoregulatory properties of cannabinoids, the endocannabinoid system (ECS) may have an important role in shaping the TME.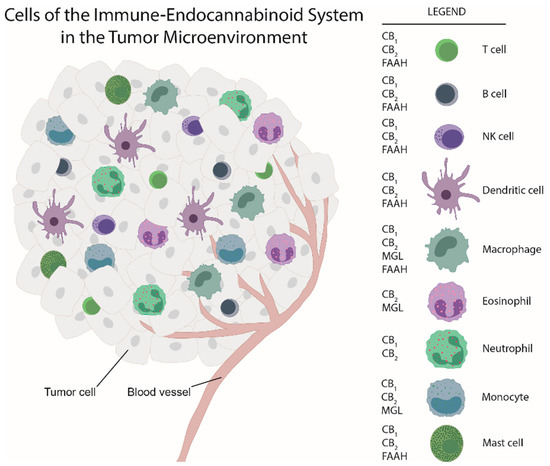
 “There is not a single pharmacological agent with demonstrated therapeutic efficacy for traumatic brain injury (TBI). With recent legalization efforts and the growing popularity of medical cannabis, patients with TBI will inevitably consider medical cannabis as a treatment option.
“There is not a single pharmacological agent with demonstrated therapeutic efficacy for traumatic brain injury (TBI). With recent legalization efforts and the growing popularity of medical cannabis, patients with TBI will inevitably consider medical cannabis as a treatment option. “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by structural damage, death, and functional disruption of cholinergic neurons (ChNs) as a result of intracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation, extracellular neuritic plaques, and hyperphosphorylation of protein tau (p-Tau) overtime.
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by structural damage, death, and functional disruption of cholinergic neurons (ChNs) as a result of intracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation, extracellular neuritic plaques, and hyperphosphorylation of protein tau (p-Tau) overtime. “Chronic pelvic pain (CPP) affects up to 15% of women in the United States. The endocannabinoid system is a potential pharmacological target for pelvic pain as cannabinoid receptors are highly expressed in the uterus and other nonreproductive tissues.
“Chronic pelvic pain (CPP) affects up to 15% of women in the United States. The endocannabinoid system is a potential pharmacological target for pelvic pain as cannabinoid receptors are highly expressed in the uterus and other nonreproductive tissues. “Opioid misuse and overuse has contributed to a widespread overdose crisis and many patients and physicians are considering medical cannabis to support opioid tapering and chronic pain control. Using a five-step modified Delphi process, we aimed to develop consensus-based recommendations on: 1) when and how to safely initiate and titrate cannabinoids in the presence of opioids, 2) when and how to safely taper opioids in the presence of cannabinoids, and 3) how to monitor patients and evaluate outcomes when treating with opioids and cannabinoids.
“Opioid misuse and overuse has contributed to a widespread overdose crisis and many patients and physicians are considering medical cannabis to support opioid tapering and chronic pain control. Using a five-step modified Delphi process, we aimed to develop consensus-based recommendations on: 1) when and how to safely initiate and titrate cannabinoids in the presence of opioids, 2) when and how to safely taper opioids in the presence of cannabinoids, and 3) how to monitor patients and evaluate outcomes when treating with opioids and cannabinoids.