 “The Cannabis plant contains numerous components, including cannabinoids and other active molecules. The phyto-cannabinoid activity is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Cannabinoids affect the nervous system and play significant roles in the regulation of the immune system.
“The Cannabis plant contains numerous components, including cannabinoids and other active molecules. The phyto-cannabinoid activity is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Cannabinoids affect the nervous system and play significant roles in the regulation of the immune system.
While Cannabis is not yet registered as a drug, the potential of cannabinoid-based medicines for the treatment of various conditions has led many countries to authorize their clinical use. However, the data from basic and medical research dedicated to medical Cannabis is currently limited.
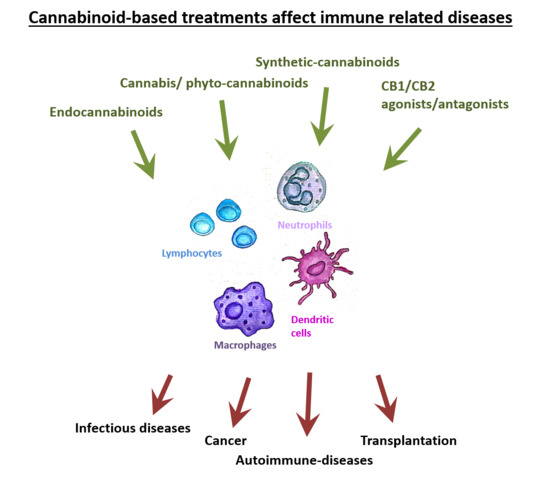
A variety of pathological conditions involve dysregulation of the immune system. For example, in cancer, immune surveillance and cancer immuno-editing result in immune tolerance. On the other hand, in autoimmune diseases increased immune activity causes tissue damage.
Immuno-modulating therapies can regulate the immune system and therefore the immune-regulatory properties of cannabinoids, suggest their use in the therapy of immune related disorders.
In this contemporary review, we discuss the roles of the endocannabinoid system in immunity and explore the emerging data about the effects of cannabinoids on the immune response in different pathologies. In addition, we discuss the complexities of using cannabinoid-based treatments in each of these conditions.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32585801/
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/12/4448

 “Current antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are undesirable for many reasons including the inability to reduce seizures in certain types of epilepsy, such as Dravet syndrome (DS) where in one-third of patients does not respond to current AEDs, and severe adverse effects that are frequently experienced by patients.
“Current antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are undesirable for many reasons including the inability to reduce seizures in certain types of epilepsy, such as Dravet syndrome (DS) where in one-third of patients does not respond to current AEDs, and severe adverse effects that are frequently experienced by patients. “Objective: To determine whether cannabis may reduce HIV-related persistent inflammation, we evaluated the relationship of cannabis use in people with HIV (PWH) to inflammatory cytokines in CSF and blood plasma.
“Objective: To determine whether cannabis may reduce HIV-related persistent inflammation, we evaluated the relationship of cannabis use in people with HIV (PWH) to inflammatory cytokines in CSF and blood plasma. “Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical
“Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical  “Cannabidiol (
“Cannabidiol ( “Painful tonic spasm (PTS) is a common yet debilitating symptom in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), especially those with longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Although carbamazepine is an effective treatment, it poses the risk of severe adverse reactions, such as Steven-Johnson syndrome (SJS).
“Painful tonic spasm (PTS) is a common yet debilitating symptom in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), especially those with longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Although carbamazepine is an effective treatment, it poses the risk of severe adverse reactions, such as Steven-Johnson syndrome (SJS). “Cannabis-inspired medical products are garnering increasing attention from the scientific community, general
“Cannabis-inspired medical products are garnering increasing attention from the scientific community, general  “The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB/Akt)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway has been associated with several pathologies in the central nervous system (CNS), including epilepsy. There is evidence supporting the hypothesis that the PI3Kγ signaling pathway may mediate the powerful anticonvulsant properties associated with the cannabinoidergic system.
“The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB/Akt)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway has been associated with several pathologies in the central nervous system (CNS), including epilepsy. There is evidence supporting the hypothesis that the PI3Kγ signaling pathway may mediate the powerful anticonvulsant properties associated with the cannabinoidergic system.