 “We used mouse microglial cells in culture activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 10 ng/ml) to study the anti-inflammatory potential of cannabidiol (CBD), the major nonpsychoactive component of cannabis.
“We used mouse microglial cells in culture activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 10 ng/ml) to study the anti-inflammatory potential of cannabidiol (CBD), the major nonpsychoactive component of cannabis.
Under LPS stimulation, CBD (1-10 μM) potently inhibited the release of prototypical proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β) and that of glutamate, a noncytokine mediator of inflammation. The effects of CBD were predominantly receptor-independent and only marginally blunted by blockade of CB2 receptors.
We established that CBD inhibited a mechanism involving, sequentially, NADPH oxidase-mediated ROS production and NF-κB-dependent signaling events. In line with these observations, active concentrations of CBD demonstrated an intrinsic free-radical scavenging capacity in the cell-free DPPH assay.
Of interest, CBD also prevented the rise in glucose uptake observed in microglial cells challenged with LPS, as did the inhibitor of NADPH oxidase apocynin and the inhibitor of IκB kinase-2, TPCA-1. This indicated that the capacity of CBD to prevent glucose uptake also contributed to its anti-inflammatory activity.
Supporting this view, the glycolytic inhibitor 2-deoxy-d-glucose (2-DG) mimicked the antioxidant/immunosuppressive effects of CBD. Interestingly, CBD and 2-DG, as well as apocynin and TPCA-1 caused a reduction in glucose-derived NADPH, a cofactor required for NADPH oxidase activation and ROS generation.
These different observations suggest that CBD exerts its anti-inflammatory effects towards microglia through an intrinsic antioxidant effect, which is amplified through inhibition of glucose-dependent NADPH synthesis.
These results also further confirm that CBD may have therapeutic utility in conditions where neuroinflammatory processes are prominent.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31647138
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/glia.23738


 “WIN55,212-2 (WIN) is a synthetic agonist of
“WIN55,212-2 (WIN) is a synthetic agonist of 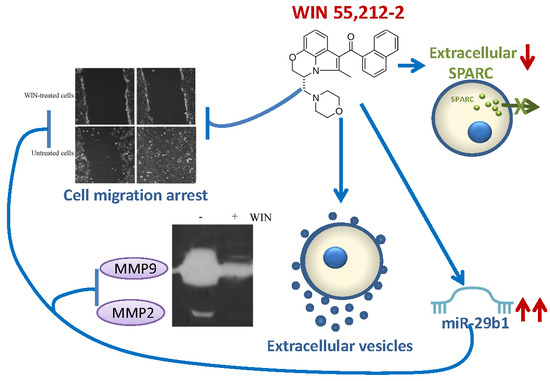
 “Hepatic fibrosis is the consequence of an unresolved wound healing process in response to chronic liver injury and involves multiple cell types and molecular mechanisms. The hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two signalling pathways with a substantial role in the liver fibrosis pathophysiology-both are upregulated in patients with advanced liver disease. Endogenous
“Hepatic fibrosis is the consequence of an unresolved wound healing process in response to chronic liver injury and involves multiple cell types and molecular mechanisms. The hepatic endocannabinoid and apelin systems are two signalling pathways with a substantial role in the liver fibrosis pathophysiology-both are upregulated in patients with advanced liver disease. Endogenous 
 “The symptomatic treatment of myotonia and myalgia in patients with dystrophic and non-dystrophic myotonias is often not satisfactory.
“The symptomatic treatment of myotonia and myalgia in patients with dystrophic and non-dystrophic myotonias is often not satisfactory.
 “Medical
“Medical  “We used mouse microglial cells in culture activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 10 ng/ml) to study the anti-inflammatory potential of
“We used mouse microglial cells in culture activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 10 ng/ml) to study the anti-inflammatory potential of  “Excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy are among the symptoms of narcolepsy, a sleep disorder caused by the loss of hypocretin/orexin (HCRT/OX) neurons placed into the hypothalamus (LH). Several treatments for managing narcolepsy include diverse drugs to induce alertness, such as antidepressants, amphetamine, or modafinil, etc.
“Excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy are among the symptoms of narcolepsy, a sleep disorder caused by the loss of hypocretin/orexin (HCRT/OX) neurons placed into the hypothalamus (LH). Several treatments for managing narcolepsy include diverse drugs to induce alertness, such as antidepressants, amphetamine, or modafinil, etc. “Although driving under the influence of cannabis is increasingly common among young adults, little is known about residual effects on driver behavior.
“Although driving under the influence of cannabis is increasingly common among young adults, little is known about residual effects on driver behavior. “Parkinson’s disease (PD) and L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia (LID) are motor disorders with significant impact on the patient’s quality of life. Unfortunately, pharmacological treatments that improve these disorders without causing severe side effects are not yet available. Delay in initiating L-DOPA is no longer recommended as LID development is a function of disease duration rather than cumulative L-DOPA exposure.
“Parkinson’s disease (PD) and L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia (LID) are motor disorders with significant impact on the patient’s quality of life. Unfortunately, pharmacological treatments that improve these disorders without causing severe side effects are not yet available. Delay in initiating L-DOPA is no longer recommended as LID development is a function of disease duration rather than cumulative L-DOPA exposure.