“Cannabinoid-based medications possess unique multimodal analgesic mechanisms of action, modulating diverse pain targets.
Cannabinoids are classified based on their origin into three categories: endocannabinoids (present endogenously in human tissues), phytocannabinoids (plant derived) and synthetic cannabinoids (pharmaceutical). Cannabinoids exert an analgesic effect, peculiarly in hyperalgesia, neuropathic pain and inflammatory states.
Endocannabinoids are released on demand from postsynaptic terminals and travels retrograde to stimulate cannabinoids receptors on presynaptic terminals, inhibiting the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. Cannabinoids (endogenous and phytocannabinoids) produce analgesia by interacting with cannabinoids receptors type 1 and 2 (CB1 and CB2), as well as putative non-CB1/CB2 receptors; G protein-coupled receptor 55, and transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1. Moreover, they modulate multiple peripheral, spinal and supraspinal nociception pathways.
Cannabinoids-opioids cross-modulation and synergy contribute significantly to tolerance and antinociceptive effects of cannabinoids. This narrative review evaluates cannabinoids’ diverse mechanisms of action as it pertains to nociception modulation relevant to the practice of anesthesiologists and pain medicine physicians.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33239391/
https://rapm.bmj.com/content/early/2020/11/24/rapm-2020-102114

 “Research within a gynecologic oncology population has lagged behind the uptake in use of medical cannabis for symptom control. This study seeks to evaluate patient experience with prescribed medical cannabis obtained through licensed dispensaries in women with gynecologic malignancies.
“Research within a gynecologic oncology population has lagged behind the uptake in use of medical cannabis for symptom control. This study seeks to evaluate patient experience with prescribed medical cannabis obtained through licensed dispensaries in women with gynecologic malignancies. “The potential therapeutic use of some Cannabis sativa plant compounds has been attracting great interest, especially for managing neuropsychiatric disorders due to the relative lack of efficacy of the current treatments.
“The potential therapeutic use of some Cannabis sativa plant compounds has been attracting great interest, especially for managing neuropsychiatric disorders due to the relative lack of efficacy of the current treatments.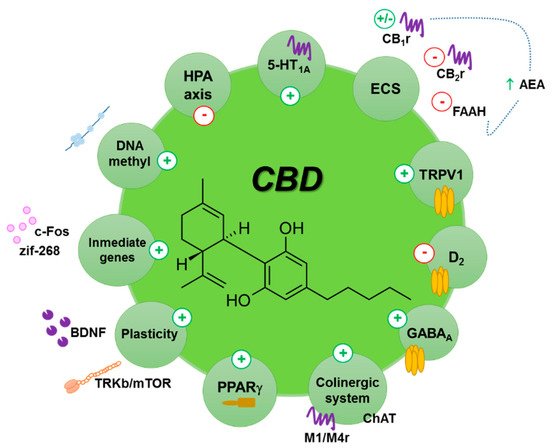
 “Little is known about the patients’ view on treatment with medical cannabis (MC) for Parkinson’s disease (PD).
“Little is known about the patients’ view on treatment with medical cannabis (MC) for Parkinson’s disease (PD). “With the current COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), there is an urgent need for new therapies and prevention strategies that can help curtail disease spread and reduce mortality.
“With the current COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), there is an urgent need for new therapies and prevention strategies that can help curtail disease spread and reduce mortality. “Objectives: To assess the motivation of cancer survivors to consume medical cannabis and to assess the patterns of use, perceived efficacy, as well as side and adverse effects.
“Objectives: To assess the motivation of cancer survivors to consume medical cannabis and to assess the patterns of use, perceived efficacy, as well as side and adverse effects. “Background: Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is characterized by progressive deterioration in behaviors, executive function and/or language. The behavioral variant (Bv) is characterized by disinhibition and obsessive/compulsive behaviors. These symptoms are sometimes resistant to medications. This series examines patients suffering with treatment-resistant Bv-FTD who were prescribed cannabinoid and related compounds for other indications.
“Background: Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is characterized by progressive deterioration in behaviors, executive function and/or language. The behavioral variant (Bv) is characterized by disinhibition and obsessive/compulsive behaviors. These symptoms are sometimes resistant to medications. This series examines patients suffering with treatment-resistant Bv-FTD who were prescribed cannabinoid and related compounds for other indications. “The increasing legalization of Cannabis for recreational and medicinal purposes in the United States has spurred renewed interest in the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids (CBs) for human disease.
“The increasing legalization of Cannabis for recreational and medicinal purposes in the United States has spurred renewed interest in the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids (CBs) for human disease. “The ability of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) inflorescence extract to counteract lipid oxidation was studied in stripped linseed oil.
“The ability of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) inflorescence extract to counteract lipid oxidation was studied in stripped linseed oil.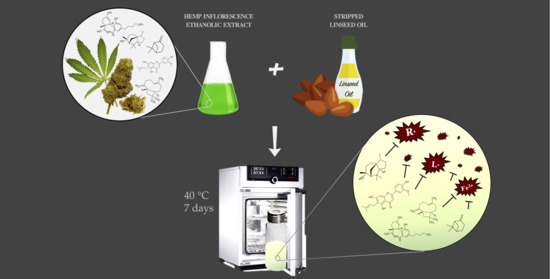
 “Cannabis has been used as a medicine for millennia. Prohibition in the mid-20th century precluded early scientific investigation.
“Cannabis has been used as a medicine for millennia. Prohibition in the mid-20th century precluded early scientific investigation.