“Rett syndrome (RTT) is a rare neurologic disorder, characterized by severe behavioural and physiological symptoms. RTT is caused by mutations in the MECP2 gene in about 95% of cases and to date no cure is available.
“Rett syndrome (RTT) is a rare neurologic disorder, characterized by severe behavioural and physiological symptoms. RTT is caused by mutations in the MECP2 gene in about 95% of cases and to date no cure is available.
Recent evidence suggests that non-euphoric phytocannabinoids (pCBs) extracted from Cannabis sativa may represent innovative therapeutic molecules for RTT, with the cannabinoid cannabidivarin having beneficial effects on behavioural and brain molecular alterations in RTT mouse models.
The present study evaluated the potential therapeutic efficacy for RTT of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA; 0.2, 2, 20 mg/kg through intraperitoneal injections for 14 days), a pCB that has proved to be effective for the treatment of nausea and anxiety in rodents.
This study demonstrates that systemic treatment with the low dose of CBDA has anti-nociceptive effects and reduces the thermal hyperalgesia in 8-month old MeCP2-308 male mice, a validated RTT mouse model. CBDA did not affect other behavioural or molecular parameters.
These results provide support to the antinociceptive effects of CBDA and stress the need for further studies aimed at clarifying the mechanisms underlying the abnormal pain perception in RTT.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33010341/
“Chronic treatment with CBDA reduces pain sensitivity in wild type mice.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306452220306254?via%3Dihub

 “Background: Little is known about medical cannabis (MC)-related care for patients with cancer using MC.
“Background: Little is known about medical cannabis (MC)-related care for patients with cancer using MC. “∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system.
“∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system. “Diabetes mellitus (DM), a metabolic disorder is one of the most prevalent chronic diseases worldwide across developed as well as developing nations. Hyperglycemia is the core feature of the type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), following insulin deficiency and impaired insulin secretion or sensitivity leads insulin resistance (IR), respectively. Genetic and environmental factors attributed to the pathogenesis of DM and various therapeutic strategies are available for the prevention and treatment of T2DM.
“Diabetes mellitus (DM), a metabolic disorder is one of the most prevalent chronic diseases worldwide across developed as well as developing nations. Hyperglycemia is the core feature of the type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), following insulin deficiency and impaired insulin secretion or sensitivity leads insulin resistance (IR), respectively. Genetic and environmental factors attributed to the pathogenesis of DM and various therapeutic strategies are available for the prevention and treatment of T2DM.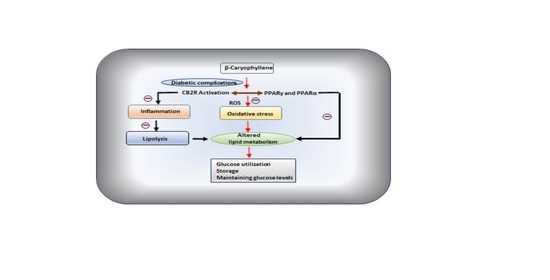
 “Studies that have analyzed the association between cannabis use and acute ischemic stroke (AIS) have provided conflicting results.
“Studies that have analyzed the association between cannabis use and acute ischemic stroke (AIS) have provided conflicting results.
 “Fibromyalgia is a complex disease process that is as prevalent as it is poorly understood. Research into the pathophysiology is ongoing, and findings will likely assist in identifying new therapeutic options to augment those in existence today that are still insufficient for the care of a large population of patients.
“Fibromyalgia is a complex disease process that is as prevalent as it is poorly understood. Research into the pathophysiology is ongoing, and findings will likely assist in identifying new therapeutic options to augment those in existence today that are still insufficient for the care of a large population of patients. “Fish oil (FO) and phytocannabinoids have received considerable attention for their intestinal anti-inflammatory effects.
“Fish oil (FO) and phytocannabinoids have received considerable attention for their intestinal anti-inflammatory effects. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is known for its vasorelaxant (including in the human pulmonary artery), anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of our study was to examine the potential preventive effect of chronic CBD administration (10 mg/kg/day for three weeks) on monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) rats.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is known for its vasorelaxant (including in the human pulmonary artery), anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of our study was to examine the potential preventive effect of chronic CBD administration (10 mg/kg/day for three weeks) on monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) rats.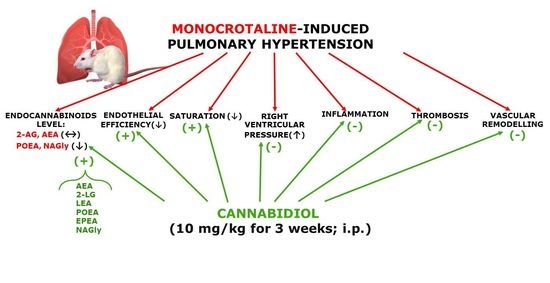
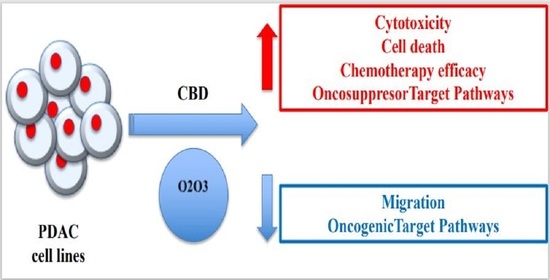
 “Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.
“Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.