 “New neuroprotective treatments of natural origin are being investigated. Both, plant extracts and isolated compounds have shown bioactive effects.
“New neuroprotective treatments of natural origin are being investigated. Both, plant extracts and isolated compounds have shown bioactive effects.
Hempseed is known for its composition of fatty acids, proteins, fibre, vitamins, as well as a large number of phytochemical compounds. After a defatting process of the seeds, hydroxycinnamic acids and its amine derivatives are the majoritarian compounds in an ethyl acetate fraction (EAF).
In the present study, we investigated in vitro effect on neuronal enzymes: MAO-A, MAO-B, tyrosinase and acetylcholinesterase. Besides, the effect of EAF on striatal biogenic amines in mice was evaluated. Both, EAF and isolated compounds (N-trans-caffeoyltyramine and N-trans-coumaroyltyramine), showed inhibitory action on MAO-A, MAO-B and tyrosinase. Furthermore, an increasing of biogenic amines was observed in the corpus striatum of the mice, after administration of EAF.
These findings show that EAF and the hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives may represent a potential treatment in degenerative neuronal diseases.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32664762/
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/09637486.2020.1793305?journalCode=iijf20


 “Thirty years ago, the discovery of a cannabinoid (CB) receptor that interacts with the psychoactive compound in Cannabis led to the identification of anandamide, an endogenous receptor ligand or endocannabinoid. Research on endocannabinoids has since exploded, and additional receptors along with their lipid mediators and signaling pathways continue to be revealed. Specifically, in humans, the release of endocannabinoids from membrane lipids occurs on demand and the signaling process is rapidly attenuated by the breakdown of the ligand suggesting a tight regulation of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Additionally, the varying distribution of CB receptors between the central nervous system and other tissues allows for the ECS to participate in a wide range of cognitive and physiological processes. Select plant-derived ‘phyto’cannabinoids such as Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) bind to the CB receptors and trigger the ECS, and in the case of Δ9-THC, while it has therapeutic value, can also produce detrimental effects. Current research is aimed at the identification of additional phytocannabinoids with minimal psychotropic effects with potential for therapeutic development. Although decades of research on the ECS and its components have expanded our understanding of the mechanisms and implications of endocannabinoid signaling in mammals, it continues to evolve. Here, we provide a brief overview of the ECS and its overlap with other related lipid-mediated signaling pathways.”
“Thirty years ago, the discovery of a cannabinoid (CB) receptor that interacts with the psychoactive compound in Cannabis led to the identification of anandamide, an endogenous receptor ligand or endocannabinoid. Research on endocannabinoids has since exploded, and additional receptors along with their lipid mediators and signaling pathways continue to be revealed. Specifically, in humans, the release of endocannabinoids from membrane lipids occurs on demand and the signaling process is rapidly attenuated by the breakdown of the ligand suggesting a tight regulation of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Additionally, the varying distribution of CB receptors between the central nervous system and other tissues allows for the ECS to participate in a wide range of cognitive and physiological processes. Select plant-derived ‘phyto’cannabinoids such as Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) bind to the CB receptors and trigger the ECS, and in the case of Δ9-THC, while it has therapeutic value, can also produce detrimental effects. Current research is aimed at the identification of additional phytocannabinoids with minimal psychotropic effects with potential for therapeutic development. Although decades of research on the ECS and its components have expanded our understanding of the mechanisms and implications of endocannabinoid signaling in mammals, it continues to evolve. Here, we provide a brief overview of the ECS and its overlap with other related lipid-mediated signaling pathways.”
 “Methamphetamine (METH) is a highly addictive psychostimulant.
“Methamphetamine (METH) is a highly addictive psychostimulant. “The compounds present in cannabis have been in use for both recreational and medicinal purposes for many centuries. Changes in the legislation in South Africa have led to an increase in the number of people interested in using these compounds for self-medication. Many of them may approach their general practitioner as the first source of information about possible therapeutic effects. It is important that medical professionals are able to give patients the correct information. Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the main compounds in cannabis plants, and there is evidence that it can successfully treat certain patients with epilepsy. This review looks at the most recent evidence on the use of CBD in the treatment of epilepsy and explores the mechanisms behind these beneficial effects.”
“The compounds present in cannabis have been in use for both recreational and medicinal purposes for many centuries. Changes in the legislation in South Africa have led to an increase in the number of people interested in using these compounds for self-medication. Many of them may approach their general practitioner as the first source of information about possible therapeutic effects. It is important that medical professionals are able to give patients the correct information. Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the main compounds in cannabis plants, and there is evidence that it can successfully treat certain patients with epilepsy. This review looks at the most recent evidence on the use of CBD in the treatment of epilepsy and explores the mechanisms behind these beneficial effects.” “In this study, we report the potential of cannabidiol, one of the major cannabis constituents, for enhancing osteoblastic differentiation in U2OS and MG-63 cells.
“In this study, we report the potential of cannabidiol, one of the major cannabis constituents, for enhancing osteoblastic differentiation in U2OS and MG-63 cells. “Highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) (approved as Epidiolex® in the United States) has demonstrated efficacy with an acceptable safety profile in patients with Lennox-Gastaut or Dravet syndrome in four randomized controlled trials. CBD possesses affinity for many target classes with functional effects relevant to the pathophysiology of many disease types, including epilepsy.
“Highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) (approved as Epidiolex® in the United States) has demonstrated efficacy with an acceptable safety profile in patients with Lennox-Gastaut or Dravet syndrome in four randomized controlled trials. CBD possesses affinity for many target classes with functional effects relevant to the pathophysiology of many disease types, including epilepsy. “A post-antibiotic world is fast becoming a reality, given the rapid emergence of pathogens that are resistant to current drugs. Therefore, there is an urgent need to discover new classes of potent antimicrobial agents with novel modes of action.
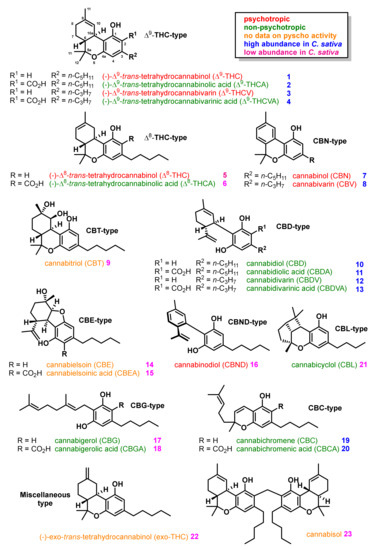
“A post-antibiotic world is fast becoming a reality, given the rapid emergence of pathogens that are resistant to current drugs. Therefore, there is an urgent need to discover new classes of potent antimicrobial agents with novel modes of action.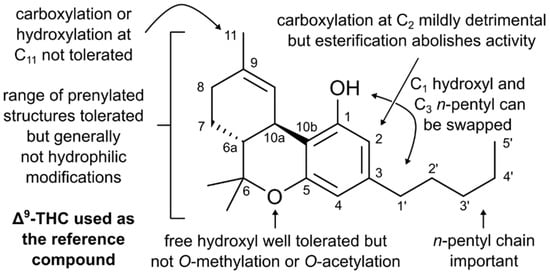

 “HIV/SIV-associated oral mucosal disease/dysfunction (HAOMD) (gingivitis/periodontitis/salivary adenitis) represents a major comorbidity affecting HIV patients on anti-retroviral therapy.
“HIV/SIV-associated oral mucosal disease/dysfunction (HAOMD) (gingivitis/periodontitis/salivary adenitis) represents a major comorbidity affecting HIV patients on anti-retroviral therapy.