 “In the last decade, we have observed an increased public and scientific interest in the clinical applications of medical cannabis.
“In the last decade, we have observed an increased public and scientific interest in the clinical applications of medical cannabis.
Currently, the application of cannabinoids in cancer patients is mainly due to their analgesic and anti-emetic effects.
The direct effects of phyto-cannabinoids on cancer cells are under intensive research, and the data remain somewhat inconsistent. Although anti-proliferative properties were observed in vitro, conclusive data from animal models and clinical trials are lacking.
Since immunotherapy of malignant diseases and bone marrow transplantation are integral approaches in hemato-oncology, the immuno-modulatory characteristic of cannabinoids is a fundamental aspect for consideration. The effect of cannabinoids on the immune system is presently under investigation, and some evidence for its immuno-regulatory properties has been shown.
In addition, the interaction of cannabinoids and classical cytotoxic agents is a subject for further investigation. Here we discuss the current knowledge of cannabinoid-based treatments in preclinical models and the limited data in oncological patients. Particularly, we address the possible contradiction between the direct anti-tumor and the immune-modulatory effects of cannabinoids.
Better understanding of the mechanism of cannabinoids influence is essential to design therapies that will allow cannabinoids to be incorporated into the clinic.”

 “The spread of antimicrobial resistance continues to be a priority health concern worldwide, necessitating exploration of alternative therapies.
“The spread of antimicrobial resistance continues to be a priority health concern worldwide, necessitating exploration of alternative therapies. “Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.
“Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.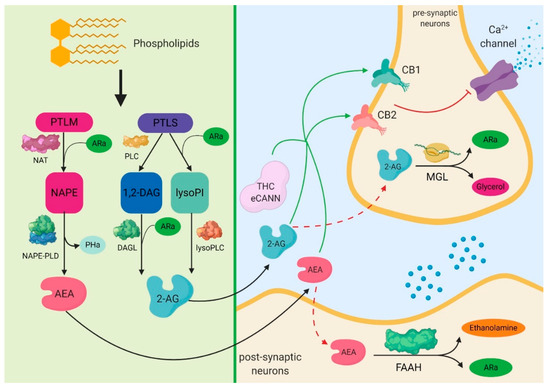
 “Beta-caryophyllene (BCP) is a flavoring agent, whereas l-arginine (LA) is used as a food supplement.
“Beta-caryophyllene (BCP) is a flavoring agent, whereas l-arginine (LA) is used as a food supplement. “The legalization of
“The legalization of  “This study aims to determine the frequency of coronary artery disease among young to middle aged adults presenting with chest pain who currently use marijuana as compared to nonusers.
“This study aims to determine the frequency of coronary artery disease among young to middle aged adults presenting with chest pain who currently use marijuana as compared to nonusers. “Endo-, phyto- and synthetic cannabinoids have been proposed as promising anti-cancer agents able to impair cancer cells’ behavior without affecting their non-transformed counterparts.
“Endo-, phyto- and synthetic cannabinoids have been proposed as promising anti-cancer agents able to impair cancer cells’ behavior without affecting their non-transformed counterparts.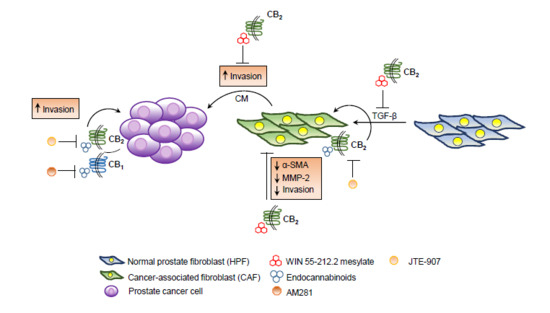
 “Recent evidence suggests that
“Recent evidence suggests that  “Medical marijuana is becoming widely available to patients in the U.S. and with recreational marijuana now legalized in many states, patient interest is on the rise.
“Medical marijuana is becoming widely available to patients in the U.S. and with recreational marijuana now legalized in many states, patient interest is on the rise. “Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) global burden is underestimated despite its high prevalence. It’s a gastrointestinal disease having obscure pathophysiology with multiple therapies yet unsatisfactory remedies.
“Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) global burden is underestimated despite its high prevalence. It’s a gastrointestinal disease having obscure pathophysiology with multiple therapies yet unsatisfactory remedies.