 “Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.
“Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.
Both exogenous and endogenous CBs carry out a variety of physiological functions by engaging with two CB receptors, the CB1 and CB2 receptors, in the human endocannabinoid system (ECS). Both CB1 and CB2 are G protein-coupled receptors that share a 7-transmembrane (7TM) topology. CB1, known as the central CB receptor, is mainly distributed in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system. CB1 activation in the human body typically promotes the release of neurotransmitters, controls pain and memory learning, and regulates metabolism and the cardiovascular system.
Clinically, CB1 is a direct drug target for drug addiction, neurodegenerative diseases, pain, epilepsy, and obesity. Unlike the exclusive expression of CB1 in the nervous system, CB2 is mainly distributed in peripheral immune cells. Selective CB2 agonists would have therapeutic potential in the treatment of inflammation and pain and avoid side effects caused by currently used clinical drugs.
Although significant progress has been made in developing agonists toward CB receptors, efficient clinical drugs targeting CB receptors remain lacking due to their complex signaling mechanisms. The recent structural elucidation of CB receptors has greatly aided our understanding of the activation and signal transduction mechanisms of CB receptors.
Recent structural characterizations of CB receptors will greatly facilitate the design of new ligands to modulate the selective functions of CB receptors. Notably, the CBD was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2018 to treat epilepsy. We now look forward to more drugs targeting these two CB receptors for clinical usage in the near future.”
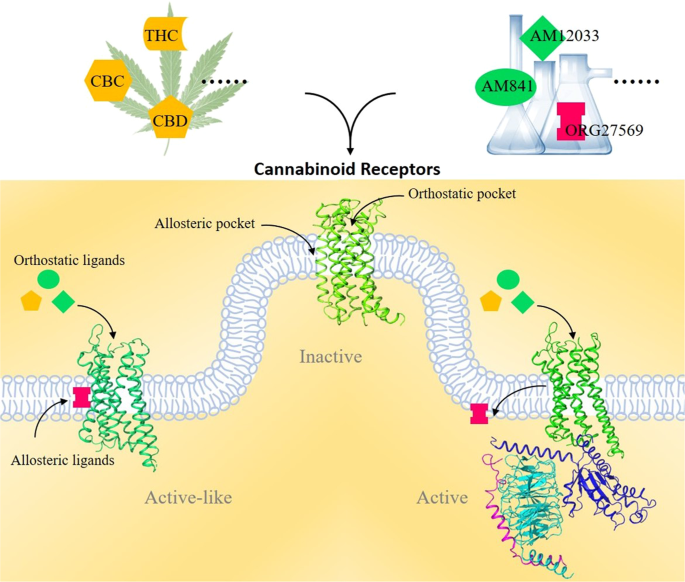

 “Like most modern molecular biology and natural product chemistry, understanding cannabinoid pharmacology centers around molecular interactions, in this case, between the cannabinoids and their putative targets, the G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). Understanding the complex structure and interplay between the partners in this molecular dance is required to understand the mechanism of action of synthetic, endogenous, and phytochemical cannabinoids. This review, with 91 references, surveys our understanding of the structural biology of the cannabinoids and their target receptors including both a critical comparison of the extant crystal structures and the computationally derived homology models, as well as an in-depth discussion about the binding modes of the major cannabinoids. The aim is to assist in situating structural biochemists, synthetic chemists, and molecular biologists who are new to the field of cannabis research.”
“Like most modern molecular biology and natural product chemistry, understanding cannabinoid pharmacology centers around molecular interactions, in this case, between the cannabinoids and their putative targets, the G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). Understanding the complex structure and interplay between the partners in this molecular dance is required to understand the mechanism of action of synthetic, endogenous, and phytochemical cannabinoids. This review, with 91 references, surveys our understanding of the structural biology of the cannabinoids and their target receptors including both a critical comparison of the extant crystal structures and the computationally derived homology models, as well as an in-depth discussion about the binding modes of the major cannabinoids. The aim is to assist in situating structural biochemists, synthetic chemists, and molecular biologists who are new to the field of cannabis research.” “Astrocytomas, the most prevalent primary brain tumors, can be divided by histology and malignancy levels into four following types: pilocytic astrocytoma (grade I), diffuse fibrillary astrocytoma (grade II), anaplastic astrocytoma (grade III), and glioblastoma multiforme (grade IV). For high grade astrocytomas (grade III and grade IV), blood vessels formation is considered as the most important property.
“Astrocytomas, the most prevalent primary brain tumors, can be divided by histology and malignancy levels into four following types: pilocytic astrocytoma (grade I), diffuse fibrillary astrocytoma (grade II), anaplastic astrocytoma (grade III), and glioblastoma multiforme (grade IV). For high grade astrocytomas (grade III and grade IV), blood vessels formation is considered as the most important property. “Painful tonic spasm (PTS) is a common yet debilitating symptom in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), especially those with longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Although carbamazepine is an effective treatment, it poses the risk of severe adverse reactions, such as Steven-Johnson syndrome (SJS).
“Painful tonic spasm (PTS) is a common yet debilitating symptom in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), especially those with longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Although carbamazepine is an effective treatment, it poses the risk of severe adverse reactions, such as Steven-Johnson syndrome (SJS). “The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB/Akt)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway has been associated with several pathologies in the central nervous system (CNS), including epilepsy. There is evidence supporting the hypothesis that the PI3Kγ signaling pathway may mediate the powerful anticonvulsant properties associated with the cannabinoidergic system.
“The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB/Akt)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway has been associated with several pathologies in the central nervous system (CNS), including epilepsy. There is evidence supporting the hypothesis that the PI3Kγ signaling pathway may mediate the powerful anticonvulsant properties associated with the cannabinoidergic system. “The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.
“The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.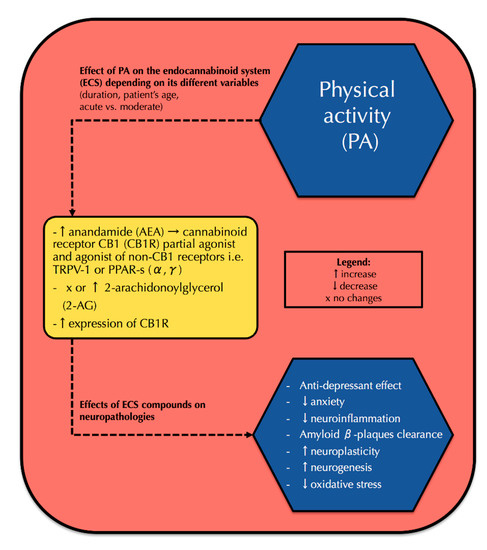
 “Alcohol use disorders affect millions of people worldwide and there is growing evidence that excessive alcohol intake causes severe damage to the brain of both humans and animals.
“Alcohol use disorders affect millions of people worldwide and there is growing evidence that excessive alcohol intake causes severe damage to the brain of both humans and animals. “Obesity rates are increasing worldwide and there is a need for novel therapeutic treatment options.
“Obesity rates are increasing worldwide and there is a need for novel therapeutic treatment options. “Δ9‐THCA‐A, the precursor of Δ9‐THC, is a non‐psychotropic phytocannabinoid that shows PPARγ agonistic activity. Herein, we investigated Δ9‐THCA ability to modulate classic cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) and evaluated its anti‐arthritis activity.
“Δ9‐THCA‐A, the precursor of Δ9‐THC, is a non‐psychotropic phytocannabinoid that shows PPARγ agonistic activity. Herein, we investigated Δ9‐THCA ability to modulate classic cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) and evaluated its anti‐arthritis activity.