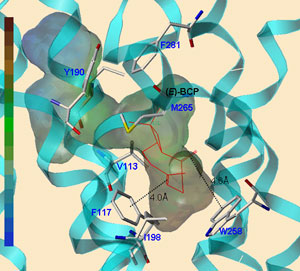
“The cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2), is a class A GPCR that was cloned in 1993 while looking for an alternate receptor that could explain the pharmacological properties of 9- tetrahydrocannabinol. CB2 was identified among cDNAs based on its similarity in amino-acid sequence to the CB1 receptor and helped provide an explanation for the established effects of cannabinoids on the immune system.
In addition to the immune system, CB2 has widespread tissue expression and has been found in brain, PNS and GI tract. Several “mixed” cannabinoid agonists are currently in clinical use primarily for controlling pain and it is believed that selective CB2 agonism may afford a superior analgesic agent devoid of the centrally mediated CB1 effects.
Thus, selective CB2 receptor agonists represent high value putative therapeutics for treating pain and other disease states. In this perspective, we seek to provide a concise update of progress in the field.”