
“Medications that improve pain threshold can be useful in the pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Pain is a prevalent PD’s non-motor symptom with a higher prevalence of analgesic drugs prescription for patients. However, specific therapy for PD-related pain are not available.
Since the endocannabinoid system is expressed extensively in different levels of pain pathway, drugs designed to target this system have promising therapeutic potential in the modulation of pain. Thus, we examined the effects of the 6-hydroxydopamine- induced PD on nociceptive responses of mice and the influence of cannabidiol (CBD) on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced nociception.
Further, we investigated the pathway involved in the analgesic effect of the CBD through the co-administration with a fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitor, increasing the endogenous anandamide levels, and possible targets from anandamide, i.e., the cannabinoid receptors subtype 1 and 2 (CB1 and CB2) and the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1).
We report that 6-hydroxydopamine- induced parkinsonism decreases the thermal and mechanical nociceptive threshold, whereas CBD (acute and chronic treatment) reduces this hyperalgesia and allodynia evoked by 6-hydroxydopamine. Moreover, ineffective doses of either FAAH inhibitor or TRPV1 receptor antagonist potentialized the CBD-evoked antinociception while an inverse agonist of the CB1 and CB2 receptor prevented the antinociceptive effect of the CBD.
Altogether, these results indicate that CBD can be a useful drug to prevent the parkinsonism-induced nociceptive threshold reduction. They also suggest that CB1 and TRPV1 receptors are important for CBD-induced analgesia and that CBD could produce these analgesic effects increasing endogenous anandamide levels.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31706993
“The CBD treatment decreases hyperalgesia and allodynia in experimental parkinsonism.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0028390819303703?via%3Dihub


 “According to recent studies,
“According to recent studies, 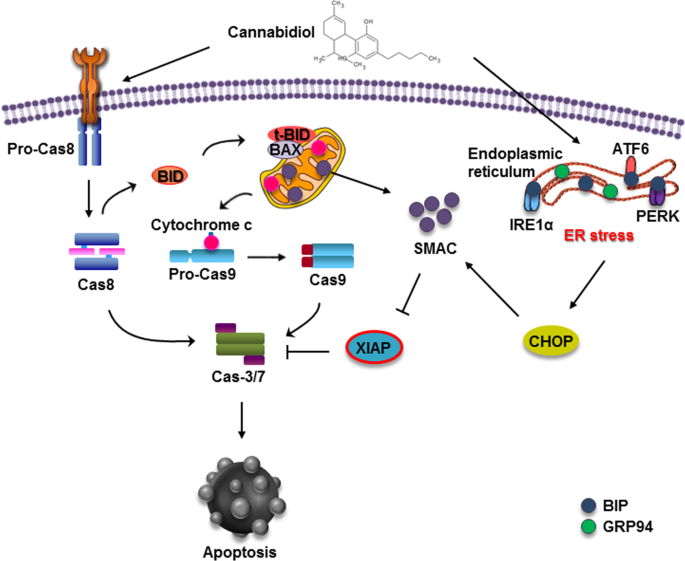
 “The healing properties of
“The healing properties of  “EpidiolexTM , a form of highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) derived from
“EpidiolexTM , a form of highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) derived from  “Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown by our laboratory to attenuate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS).
“Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown by our laboratory to attenuate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS). “The symptomatic treatment of myotonia and myalgia in patients with dystrophic and non-dystrophic myotonias is often not satisfactory.
“The symptomatic treatment of myotonia and myalgia in patients with dystrophic and non-dystrophic myotonias is often not satisfactory.
 “We used mouse microglial cells in culture activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 10 ng/ml) to study the anti-inflammatory potential of
“We used mouse microglial cells in culture activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 10 ng/ml) to study the anti-inflammatory potential of  “Excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy are among the symptoms of narcolepsy, a sleep disorder caused by the loss of hypocretin/orexin (HCRT/OX) neurons placed into the hypothalamus (LH). Several treatments for managing narcolepsy include diverse drugs to induce alertness, such as antidepressants, amphetamine, or modafinil, etc.
“Excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy are among the symptoms of narcolepsy, a sleep disorder caused by the loss of hypocretin/orexin (HCRT/OX) neurons placed into the hypothalamus (LH). Several treatments for managing narcolepsy include diverse drugs to induce alertness, such as antidepressants, amphetamine, or modafinil, etc.