 “UV phototherapy used in chronic skin diseases causes redox imbalance and pro-inflammatory reactions, especially in the case of unchanged skin cells.
“UV phototherapy used in chronic skin diseases causes redox imbalance and pro-inflammatory reactions, especially in the case of unchanged skin cells.
To prevent the harmful effects of UV radiation, cannabidiol (CBD) has been used, which has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of CBD on the metabolism of skin keratinocytes in nude rats exposed to UVA/UVB radiation using a proteomic approach.
The results obtained with SDS-PAGE/nanoHPLC/QexactiveOrbiTrap show that exposure of rat’s skin to UVA/UVB radiation, as well as the action of CBD, significantly modified the expression of proteins involved in inflammation, redox balance and apoptosis.
UVA/UVB radiation significantly increased the expression and biological effectiveness of the nuclear factor associated with erythroid factor 2 (Nrf2) and cytoprotective proteins being products of its transcriptional activity, including superoxide dismutase (Cu,Zn-SOD) and the inflammatory response (nuclear receptor coactivator-3 and paralemmin-3), while CBD treatment counteracted and partially eliminated these changes.
Moreover, cannabidiol reversed changes in the UV-induced apoptotic pathways by modifying anti-apoptotic and pro-apoptotic factors (apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 and transforming growth factor-β).
The results show that CBD maintains keratinocyte proteostasis and therefore could be suggested as a protective measure in the prevention of UV-induced metabolic changes in epidermal keratinocytes.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33086172/
“In summary, UVA and UVB radiation affect the proteomic profile of keratinocytes of healthy rat skin in different ways. Both types of radiation change the level of proteins involved in the regulation of cellular redox balance, inflammation, and apoptosis. In contrast, topical application of CBD to rat skin, when exposed to UV radiation, helps normalize the expression of keratinocyte proteins that are metabolically relevant by modeling their biosynthesis and degradation. Thus, CBD can maintain the proteostasis of keratinocytes. Because UV therapy is a part of the treatment of skin diseases, e.g. psoriasis, the use of CBD on unchanged skin may be suggested as a protective factor to reduce the metabolic changes caused by UV radiation in unchanged keratinocytes. This suggestion is particularly important when the beneficial effect of cannabidiol on psoriasis-induced skin lesions has recently also been confirmed.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0731708520315429?via%3Dihub
 “Cannabinoids have been found to be effective in controlling seizures and the highly purified form of cannabinoid derived for Cannabis sativa . Cannabidiol (CBD) is now approved for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) and Dravet syndrome. CBD was used in a 9-year-old boy with LGS (unknown etiology) with very good results. The electroencephalography (EEG) response was very dramatic with near normalization of EEG background and complete control of seizures. The effect of CBD on EEG with such an improvement has not been described previously. Also, this adds to evidence that early intervention in LGS with CBD might be more helpful and improve outcomes.”
“Cannabinoids have been found to be effective in controlling seizures and the highly purified form of cannabinoid derived for Cannabis sativa . Cannabidiol (CBD) is now approved for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) and Dravet syndrome. CBD was used in a 9-year-old boy with LGS (unknown etiology) with very good results. The electroencephalography (EEG) response was very dramatic with near normalization of EEG background and complete control of seizures. The effect of CBD on EEG with such an improvement has not been described previously. Also, this adds to evidence that early intervention in LGS with CBD might be more helpful and improve outcomes.”
 “The anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids including CBD (Cannabidiol) and THC ((-)-trans-∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol) have been reported in the case of pancreatic cancer (PC).
“The anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids including CBD (Cannabidiol) and THC ((-)-trans-∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol) have been reported in the case of pancreatic cancer (PC). “Cocaine addiction is a global health problem with no approved pharmacotherapies.
“Cocaine addiction is a global health problem with no approved pharmacotherapies. “Many people with MS (pwMS) use unregulated cannabis or cannabis products to treat the symptoms associated with the disease. In line with this, Sativex, a synthetic combination of cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) has been approved to treat symptoms of spasticity.
“Many people with MS (pwMS) use unregulated cannabis or cannabis products to treat the symptoms associated with the disease. In line with this, Sativex, a synthetic combination of cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) has been approved to treat symptoms of spasticity.
 “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a central nervous system disease characterized by dementia, which has now become a major threat to global health.
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a central nervous system disease characterized by dementia, which has now become a major threat to global health. “The prevalence of cancer pain will continue to rise as pain is common among the survivorship and general cancer population. As interest in cannabis and cannabinoids for medicinal use including pain management continues to rise, there is growing need to update and review the current state of evidence for their use. The literature was searched for articles in English with key words cannabis, cannabinoids, and cancer pain. The sources of articles were PubMed, Embase, and open Google search.
“The prevalence of cancer pain will continue to rise as pain is common among the survivorship and general cancer population. As interest in cannabis and cannabinoids for medicinal use including pain management continues to rise, there is growing need to update and review the current state of evidence for their use. The literature was searched for articles in English with key words cannabis, cannabinoids, and cancer pain. The sources of articles were PubMed, Embase, and open Google search. “Voltage-gated sodium channels are targets for a range of pharmaceutical drugs developed for treatment of neurological diseases.
“Voltage-gated sodium channels are targets for a range of pharmaceutical drugs developed for treatment of neurological diseases. “These data support the notion that CBD and CBDV act as functional partial agonists on dopamine D2-like receptors in vivo.
“These data support the notion that CBD and CBDV act as functional partial agonists on dopamine D2-like receptors in vivo. “In this proof-of-concept study, the antioxidant activity of phytocannabinoids, namely cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), were investigated using an in vitro system of differentiated human neuronal SY-SH5Y cells.
“In this proof-of-concept study, the antioxidant activity of phytocannabinoids, namely cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), were investigated using an in vitro system of differentiated human neuronal SY-SH5Y cells.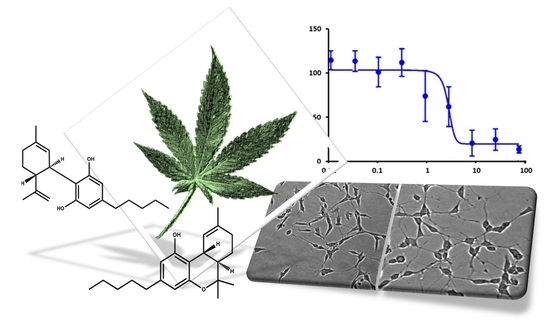
 “UV phototherapy used in chronic skin diseases causes redox imbalance and pro-inflammatory reactions, especially in the case of unchanged skin cells.
“UV phototherapy used in chronic skin diseases causes redox imbalance and pro-inflammatory reactions, especially in the case of unchanged skin cells.