
“Breast cancer (BC) is the second most prevalent cancer worldwide.
Estrogen receptor beta (ERβ) is an essential protein of breast cells to suppress estrogen induced uncontrolled proliferation. Thus small molecules that can modulate and enhance ERβ expression would be an effective agent to suppress BC development.
Studies showed that cannabinoid (CB), specifically Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Del9THC), can increase the expression of ERβ and inhibits BC cell proliferation.
In this study, less psychoactive and structurally similar analogues of Del9THC were chosen as drug candidates and ERβ was targeted as a therapeutic receptor. Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Del8THC) and Delta-4-Isotetrahydrocannabinol (Del4isoTHC) were the drug candidates selected on the basis of literature reports, Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion and Toxicity (ADMET) properties, medicinal chemistry profile and physicochemical features.
Molecular docking simulations were carried out to determine ligand receptor interactions and binding affinity based on free binding energy. To get a better drug, the structural modification was done on Del8THC and generated a new CB analogue called Cannabinoid A.
Finally, molecular interaction analysis revealed that two CBs and one of their analogue interact with the active site residues of ERβ. Therefore, this study revealed a new way to discover novel drug(s) for BC patients.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32116130
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/07391102.2020.1737233?journalCode=tbsd20

 “The 20% prevalence of chronic pain in the general population is a major health concern given the often profound associated impairment of daily activities, employment status, and health-related quality of life in sufferers. Resource utilization associated with chronic pain represents an enormous burden for healthcare systems. Although analgesia based on the World Health Organization’s pain ladder continues to be the mainstay of chronic pain management, aside from chronic cancer pain or end-of-life care, prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioids to manage chronic pain is rarely sustainable.
“The 20% prevalence of chronic pain in the general population is a major health concern given the often profound associated impairment of daily activities, employment status, and health-related quality of life in sufferers. Resource utilization associated with chronic pain represents an enormous burden for healthcare systems. Although analgesia based on the World Health Organization’s pain ladder continues to be the mainstay of chronic pain management, aside from chronic cancer pain or end-of-life care, prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or opioids to manage chronic pain is rarely sustainable. “To determine whether differences in disability status, spasticity severity, and spasticity duration at treatment start in patients with resistant multiple sclerosis (MS) spasticity might influence response to add-on tetrahydrocannabinol:
“To determine whether differences in disability status, spasticity severity, and spasticity duration at treatment start in patients with resistant multiple sclerosis (MS) spasticity might influence response to add-on tetrahydrocannabinol: “Radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy is the major treatment modality for human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). GBMs eventually relapse after treatment and the average survival of GBM patients is less than two years.
“Radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy is the major treatment modality for human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). GBMs eventually relapse after treatment and the average survival of GBM patients is less than two years. “Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g.,
“Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g.,  “Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.
“Critically ill patients with sepsis require a multidisciplinary approach, as this situation implies multiorgan distress, with most of the bodily biochemical and cellular systems being affected by the condition. Moreover, sepsis is characterized by a multitude of biochemical interactions and by dynamic changes of the immune system. At the moment, there is a gap in our understanding of the cellular, genetic, and molecular mechanisms involved in sepsis.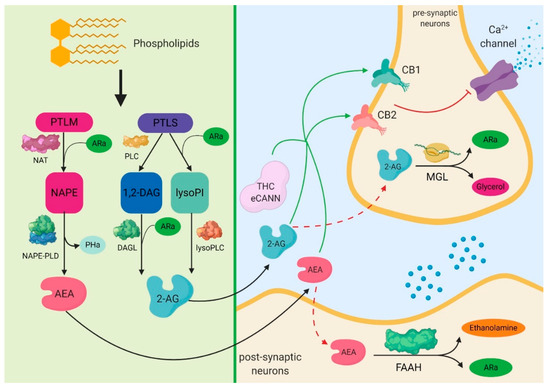
 “Palliative medicine physicians are challenged by lack of guidance regarding effectiveness and dosing of cannabis products in the setting of their emerging popularity.
“Palliative medicine physicians are challenged by lack of guidance regarding effectiveness and dosing of cannabis products in the setting of their emerging popularity. “Given the growing challenges in chronic pain management coupled with the ongoing consequences of the opioid epidemic, pain management practitioners are looking into more effective, innovative, and safer alternatives to treat pain.
“Given the growing challenges in chronic pain management coupled with the ongoing consequences of the opioid epidemic, pain management practitioners are looking into more effective, innovative, and safer alternatives to treat pain. “γ-Aminobutyric acid type A receptors (GABAARs) are the main inhibitory mediators in the central nervous system (CNS). GABAARs are pentameric ligand gated ion channels, and the main subunit composition is usually 2α2βγ, with various isotypes assembled within a set of 19 different subunits. The inhibitory function is mediated by chloride ion movement across the GABAARs, activated by synaptic GABA release, reducing neuronal excitability in the adult CNS. Several studies highlighted the importance of GABA-mediated transmission during neuro-development, and its involvement in different neurological and neurodevelopmental diseases, from anxiety to epilepsy. However, while it is well known how different classes of drugs are able to modulate the GABAARs function (benzodiazepines, barbiturates, neurosteroids, alcohol), up to now little is known about GABAARs and cannabinoids interaction in the CNS. Endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids are lately emerging as a new class of promising drugs for a wide range of neurological conditions, but their safety as medication, and their mechanisms of action are still to be fully elucidated. In this review, we will focus our attention on two of the most promising molecules (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol; Δ9-THC and
“γ-Aminobutyric acid type A receptors (GABAARs) are the main inhibitory mediators in the central nervous system (CNS). GABAARs are pentameric ligand gated ion channels, and the main subunit composition is usually 2α2βγ, with various isotypes assembled within a set of 19 different subunits. The inhibitory function is mediated by chloride ion movement across the GABAARs, activated by synaptic GABA release, reducing neuronal excitability in the adult CNS. Several studies highlighted the importance of GABA-mediated transmission during neuro-development, and its involvement in different neurological and neurodevelopmental diseases, from anxiety to epilepsy. However, while it is well known how different classes of drugs are able to modulate the GABAARs function (benzodiazepines, barbiturates, neurosteroids, alcohol), up to now little is known about GABAARs and cannabinoids interaction in the CNS. Endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids are lately emerging as a new class of promising drugs for a wide range of neurological conditions, but their safety as medication, and their mechanisms of action are still to be fully elucidated. In this review, we will focus our attention on two of the most promising molecules (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol; Δ9-THC and  “It has been hypothesized that besides its intraocular pressure (IOP) lowering potential, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) may also improve ocular hemodynamics.
“It has been hypothesized that besides its intraocular pressure (IOP) lowering potential, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) may also improve ocular hemodynamics.