 “Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
“Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a ubiquitous signalling system that is theorised to be dysregulated within wound beds and associated peri-wound tissues.
Preclinical research has shown that the dominant chemical classes derived from the cannabis plant, cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids, interact with the integumentary ECS to promote wound closure and analgesia.
This is a prospective open label cohort study involving two elderly Caucasian females with recalcitrant NUC leg ulcers of greater than 6 months duration.
Topical Cannabis-Based Medicines (TCBM) composed of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids were applied daily to both the wound bed and peri-wound tissues until complete wound closure was achieved.
Wounds were photographed regularly, and the digital images were subjected to planimetric analysis to objectively quantify the degree of granulation and epithelization. Analgesic utilisation, as a surrogate/proxy for pain scores, was also tracked. The cohort had a mean M3 multimorbidity index score of 3.31. Complete wound closure was achieved in a mean of 76.3 days. Additionally, no analgesics were required after a mean of 63 days.
The treatments were well tolerated with no adverse reactions. The positive results demonstrated in very challenging wounds such as NUC, among highly complex patients, suggest that TCBM may have an even broader role within integumentary and wound management.
This treatment paradigm warrants being trialled in other wound types and classes, and ultimately should be subjected to randomised controlled trials.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32875692/
“Topical Cannabis‐Based Medicines, applied to both wound beds and peri‐wound tissues, represent a promising novel, non‐invasive, and safe treatment option for NUC leg ulcers.”
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/iwj.13484


 “There is no argument with regard to the physical and psychological stress-related nature of neuropsychiatric disorders. Yet, the mechanisms that facilitate disease onset starting from molecular stress responses are elusive.
“There is no argument with regard to the physical and psychological stress-related nature of neuropsychiatric disorders. Yet, the mechanisms that facilitate disease onset starting from molecular stress responses are elusive.
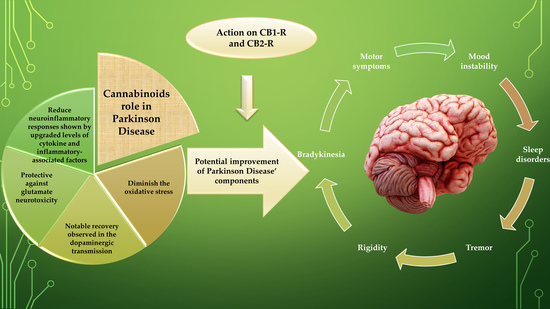
 “The endocannabinoid signaling system (ECSS) is altered by exposure to stress and mediates and modulates the effects of stress on the brain.
“The endocannabinoid signaling system (ECSS) is altered by exposure to stress and mediates and modulates the effects of stress on the brain. “Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading fast all around the world with more than fourteen millions of detected infected cases and more than 600.000 deaths by 20th July 2020. While scientist are working to find a vaccine, current epidemiological data shows that the most common comorbidities for patients with the worst prognosis, hypertension and diabetes, are often treated with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
“Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading fast all around the world with more than fourteen millions of detected infected cases and more than 600.000 deaths by 20th July 2020. While scientist are working to find a vaccine, current epidemiological data shows that the most common comorbidities for patients with the worst prognosis, hypertension and diabetes, are often treated with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an irreversible chronic neurodegenerative disorder that occurs when neurons in the brain degenerate and die. Pain frequently arises in older patients with neurodegenerative diseases including AD. However, the presence of pain in older people is usually overlooked with cognitive dysfunctions. Most of the times dementia patients experience moderate to severe pain but the development of severe cognitive dysfunctions tremendously affects their capability to express the presence of pain. Currently, there are no effective treatments against AD that emphasize the necessity for increasing research to develop novel drugs for treating or preventing the disease process. Furthermore, the prospective therapeutic use of cannabinoids in AD has been studied for the past few years. In this regard, targeting the endocannabinoid system has considered as a probable therapeutic strategy to control several associated pathological pathways, such as mitochondrial dysfunction, excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation for the management of AD. In this review, we focus on recent studies about the role of cannabinoids for the treatment of pain and related neuropathological changes in AD.”
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an irreversible chronic neurodegenerative disorder that occurs when neurons in the brain degenerate and die. Pain frequently arises in older patients with neurodegenerative diseases including AD. However, the presence of pain in older people is usually overlooked with cognitive dysfunctions. Most of the times dementia patients experience moderate to severe pain but the development of severe cognitive dysfunctions tremendously affects their capability to express the presence of pain. Currently, there are no effective treatments against AD that emphasize the necessity for increasing research to develop novel drugs for treating or preventing the disease process. Furthermore, the prospective therapeutic use of cannabinoids in AD has been studied for the past few years. In this regard, targeting the endocannabinoid system has considered as a probable therapeutic strategy to control several associated pathological pathways, such as mitochondrial dysfunction, excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation for the management of AD. In this review, we focus on recent studies about the role of cannabinoids for the treatment of pain and related neuropathological changes in AD.” “Cannabinoid receptors type 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2) are widely expressed in the human body, and are attractive drug targets in the prevention and management of central nervous system (CNS) and immune system dysfunction, respectively. Recent breakthroughs in the structural elucidation of cannabinoid receptors and their signaling complexes with G proteins, provide the important molecular basis of ligand-receptor interactions, activation and signaling mechanism, which will facilitate the next-generation drug design and the precise modulation of the endocannabinoid system. Here, we provide an overview on the structural features of cannabinoid receptors in different functional states and the diverse ligand binding modes. The major challenges and new strategies for future therapeutic applications targeting the endocannabinoid system (ECS) are also discussed.”
“Cannabinoid receptors type 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2) are widely expressed in the human body, and are attractive drug targets in the prevention and management of central nervous system (CNS) and immune system dysfunction, respectively. Recent breakthroughs in the structural elucidation of cannabinoid receptors and their signaling complexes with G proteins, provide the important molecular basis of ligand-receptor interactions, activation and signaling mechanism, which will facilitate the next-generation drug design and the precise modulation of the endocannabinoid system. Here, we provide an overview on the structural features of cannabinoid receptors in different functional states and the diverse ligand binding modes. The major challenges and new strategies for future therapeutic applications targeting the endocannabinoid system (ECS) are also discussed.” “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a multifactorial neurodegenerative disorder linked to various converging toxic mechanisms. Evidence suggests that hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation and excitotoxicity, all of which play important roles in the onset and progression of AD pathogenesis.
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a multifactorial neurodegenerative disorder linked to various converging toxic mechanisms. Evidence suggests that hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation and excitotoxicity, all of which play important roles in the onset and progression of AD pathogenesis.