 “Purpose: The endocannabinoid system has emerged as a key regulatory signaling pathway in the pathophysiology of alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD). More than 30 years of research have established different roles of endocannabinoids and their receptors in various aspects of liver diseases, such as steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. However, pharmacological applications of the endocannabinoid system for the treatment of ALD have not been successful because of psychoactive side effects, despite some beneficial effects. Thus, a more delicate and detailed elucidation of the mechanism linking the endocannabinoid system and ALD may be of paramount significance in efforts to apply the system to the treatment of ALD.
“Purpose: The endocannabinoid system has emerged as a key regulatory signaling pathway in the pathophysiology of alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD). More than 30 years of research have established different roles of endocannabinoids and their receptors in various aspects of liver diseases, such as steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. However, pharmacological applications of the endocannabinoid system for the treatment of ALD have not been successful because of psychoactive side effects, despite some beneficial effects. Thus, a more delicate and detailed elucidation of the mechanism linking the endocannabinoid system and ALD may be of paramount significance in efforts to apply the system to the treatment of ALD.
Search results: According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the authors selected 47 eligible full-text articles out of 2,691 searched initially. Studies in the past 3 decades revealed the opposite effects of cannabinoid receptors CB1R and CB2R on steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in ALD.
Discussion and conclusions: This review summarizes the endocannabinoid signaling in the general physiology of the liver, the pathogenesis of ALD, and some of the potential therapeutic implications of cannabinoid-based treatments for ALD.”
“Over the past 30 years, it has been found that the endocannabinoid system is involved in a variety of pathways associated with the onset, or the progression, of several diseases, including ALD. The endocannabinoid system has been observed in both the hepatocytes and various nonparenchymal cells in the liver, in which the endocannabinoid production and its receptor activation may contribute to the development of a spectrum of ALD, ranging from simple alcoholic steatosis to more severe forms such as steatohepatitis and fibrosis. Therefore, understanding the precise physiology of the endocannabinoid system in the liver and unveiling the mechanism underlying the association between ALD progression and hepatic endocannabinoid signaling seem to bear a paramount significance for the advancement of ALD treatment, as well as for the treatment of other chronic liver diseases (e.g., NAFLD, viral hepatitis). Moreover, developing efficacious and highly selective cannabinoid receptor–modulating drugs could be a major breakthrough in the treatment of ALD.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8496755/


 “Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) are chronic, idiopathic, inflammatory, gastrointestinal disorders.
“Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) are chronic, idiopathic, inflammatory, gastrointestinal disorders.  “Background:
“Background:  “Studies investigating the psychosomatic effects of social isolation in animals have shown that one of the physiologic system that gets disrupted by this environment-affective change is the Endocannabinoid System. As the levels of endocannabinoids change in limbic areas and prefrontal cortex during stressful times, so is the subject more prone to fearful and negative thoughts and aggressive behavior. The interplay of social isolation on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and cannabinoid tone triggers a vicious cycle which further impairs the natural body’s homeostatic neuroendocrine levels and provokes a series of risk factors for developing health complications. In this paper, we explore the psychosomatic impact of prolonged quarantine in healthy individuals, and propose management and coping strategies that may improve endocannabinoid tone, such as integration of probiotics, cannabidiol, meditation, and physical exercise interventions with the aim of supporting interpersonal, individual, and professional adherence with COVID-19 emergency public measures whilst minimizing their psycho-physical impact.”
“Studies investigating the psychosomatic effects of social isolation in animals have shown that one of the physiologic system that gets disrupted by this environment-affective change is the Endocannabinoid System. As the levels of endocannabinoids change in limbic areas and prefrontal cortex during stressful times, so is the subject more prone to fearful and negative thoughts and aggressive behavior. The interplay of social isolation on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and cannabinoid tone triggers a vicious cycle which further impairs the natural body’s homeostatic neuroendocrine levels and provokes a series of risk factors for developing health complications. In this paper, we explore the psychosomatic impact of prolonged quarantine in healthy individuals, and propose management and coping strategies that may improve endocannabinoid tone, such as integration of probiotics, cannabidiol, meditation, and physical exercise interventions with the aim of supporting interpersonal, individual, and professional adherence with COVID-19 emergency public measures whilst minimizing their psycho-physical impact.” “In humans, various sites like cannabinoid receptors (CBR) having a binding affinity with cannabinoids are distributed on the surface of different cell types, where endocannabinoids (ECs) and derivatives of fatty acid can bind. The binding of these substance(s) triggers the activation of specific receptors required for various physiological functions, including pain sensation, memory, and appetite.
“In humans, various sites like cannabinoid receptors (CBR) having a binding affinity with cannabinoids are distributed on the surface of different cell types, where endocannabinoids (ECs) and derivatives of fatty acid can bind. The binding of these substance(s) triggers the activation of specific receptors required for various physiological functions, including pain sensation, memory, and appetite. 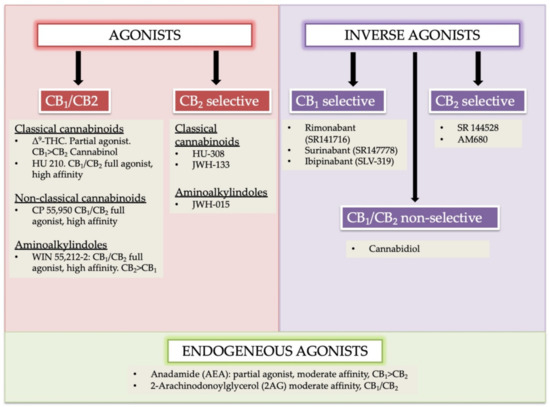
 “Chronic inflammation is considered to be a silent killer because it is the underlying cause of a wide range of clinical disorders, from cardiovascular to neurological diseases, and from cancer to obesity. In addition, there are over 80 different types of debilitating autoimmune diseases for which there are no cure. Currently, the drugs that are available to suppress chronic inflammation are either ineffective or overtly suppress the inflammation, thereby causing increased susceptibility to infections and cancer. Thus, the development of a new class of drugs that can suppress chronic inflammation is imperative.
“Chronic inflammation is considered to be a silent killer because it is the underlying cause of a wide range of clinical disorders, from cardiovascular to neurological diseases, and from cancer to obesity. In addition, there are over 80 different types of debilitating autoimmune diseases for which there are no cure. Currently, the drugs that are available to suppress chronic inflammation are either ineffective or overtly suppress the inflammation, thereby causing increased susceptibility to infections and cancer. Thus, the development of a new class of drugs that can suppress chronic inflammation is imperative. 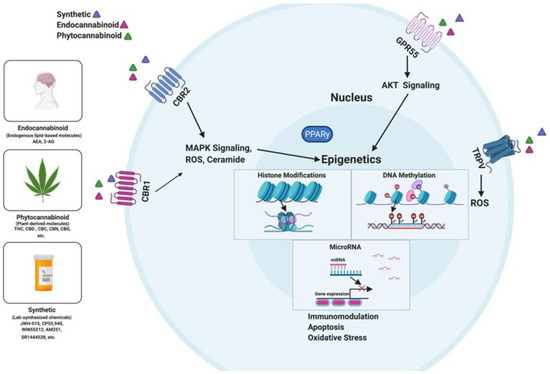
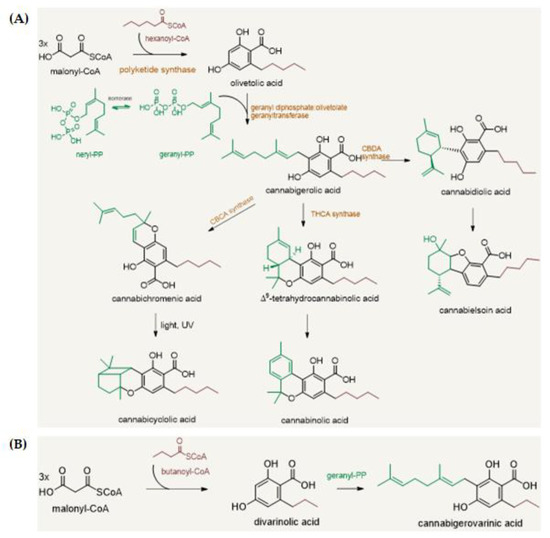
 “The therapeutic potential of
“The therapeutic potential of 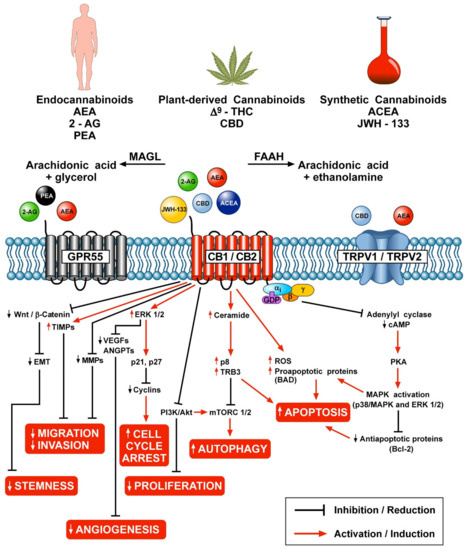
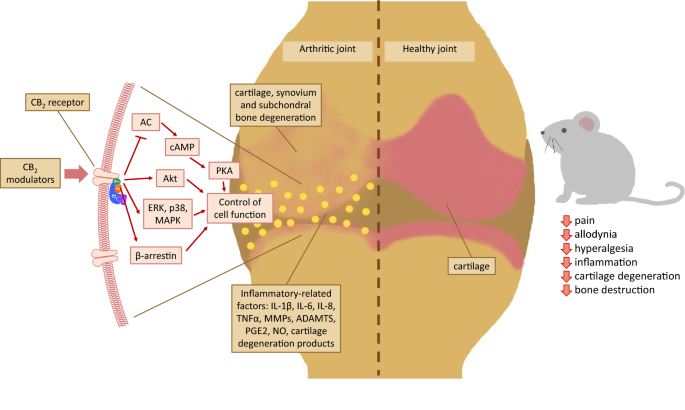 “Over the last several decades, the percentage of patients suffering from different forms of arthritis has increased due to the ageing population and the increasing risk of civilization diseases, e.g. obesity, which contributes to arthritis development. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are estimated to affect 50-60% of people over 65 years old and cause serious health and economic problems. Currently, therapeutic strategies are limited and focus mainly on pain attenuation and maintaining joint functionality. First-line therapies are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; in more advanced stages, stronger analgesics, such as opioids, are required, and in the most severe cases, joint arthroplasty is the only option to ensure joint mobility.
“Over the last several decades, the percentage of patients suffering from different forms of arthritis has increased due to the ageing population and the increasing risk of civilization diseases, e.g. obesity, which contributes to arthritis development. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are estimated to affect 50-60% of people over 65 years old and cause serious health and economic problems. Currently, therapeutic strategies are limited and focus mainly on pain attenuation and maintaining joint functionality. First-line therapies are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; in more advanced stages, stronger analgesics, such as opioids, are required, and in the most severe cases, joint arthroplasty is the only option to ensure joint mobility.  “
“