“Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.
“Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.
Oxygen-ozone (O2/O3) therapy is an emerging alternative tool for the treatment of several clinical disorders. O2/O3 therapy has been found to ameliorate mechanisms promoting chronic pain and inflammation, including hypoxia, inflammatory mediators, and infection.
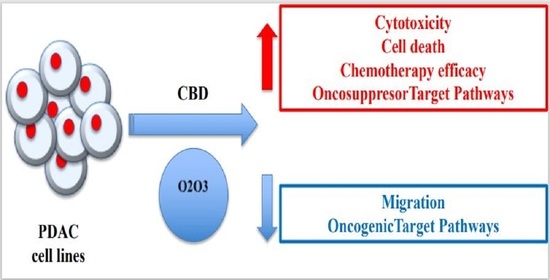
The advantages of using cannabinoids have been evaluated in vitro and in vivo models of several human cancers. Regarding PDAC, activation of cannabinoid receptors was found to induce pancreatic cancer cell apoptosis without affecting the normal pancreas cells.
In a murine model of PDAC, a combination of cannabidiol (CBD) and gemcitabine increased survival length by nearly three times. Herein, we evaluate the anticancer effect of CBD and O2/O3, alone or in combination, on two human PDAC cell lines, PANC-1 and MiaPaCa-2, examining expression profiles of 92 pancreatic adenocarcinoma associated genes, cytotoxicity, migration properties, and cell death. Finally, we assess the combination effects with gemcitabine and paclitaxel.
Summarizing, for the first time the antitumoral effect of combined therapy with CBD and oxygen-ozone therapy in PDAC is evidenced.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32992648/
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/12/10/2774

 “In recent years there has been a growing appreciation by regulatory authorities that cannabis-based medicines can play a useful role in disease therapy.
“In recent years there has been a growing appreciation by regulatory authorities that cannabis-based medicines can play a useful role in disease therapy. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is reported to produce pain relief, but the clinically relevant cellular and molecular mechanisms remain uncertain.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is reported to produce pain relief, but the clinically relevant cellular and molecular mechanisms remain uncertain. “Cannabidiol (CBD), a natural occurring phytocannabinoid, is used extensively in consumer products ranging from foods to shampoos, topical oils and lotions.
“Cannabidiol (CBD), a natural occurring phytocannabinoid, is used extensively in consumer products ranging from foods to shampoos, topical oils and lotions. “Δ9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main bioactive compound found in the plant Cannabis sativa, exerts its effects by activating cannabinoid receptors present in many neural cells.
“Δ9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main bioactive compound found in the plant Cannabis sativa, exerts its effects by activating cannabinoid receptors present in many neural cells. “Psoriasis is associated with increased production of reactive oxygen species which leads to oxidative stress.
“Psoriasis is associated with increased production of reactive oxygen species which leads to oxidative stress.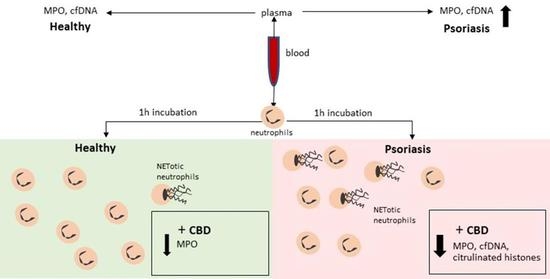
 “The pharmacological treatment for autism spectrum disorders is often poorly tolerated and has traditionally targeted associated conditions, with limited benefit for the core social deficits.
“The pharmacological treatment for autism spectrum disorders is often poorly tolerated and has traditionally targeted associated conditions, with limited benefit for the core social deficits. “Natural cannabinoids may have beneficial effects on various tissues and functions including a positive influence on the immune system and the inflammatory process.
“Natural cannabinoids may have beneficial effects on various tissues and functions including a positive influence on the immune system and the inflammatory process. “In the absence of effective antivirals and vaccination, the pandemic of COVID-19 remains the most significant challenge to our health care system in decades. There is an urgent need for definitive therapeutic intervention.
“In the absence of effective antivirals and vaccination, the pandemic of COVID-19 remains the most significant challenge to our health care system in decades. There is an urgent need for definitive therapeutic intervention.