
“Currently, an increasing number of diseases related to insulin resistance and obesity is an alarming problem worldwide. It is well-known that the above states can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases. An excessive amount of triacylglycerols (TAGs) in a diet also evokes adipocyte hyperplasia and subsequent accumulation of lipids in peripheral organs (liver, cardiac muscle). Therefore, new therapeutic methods are constantly sought for the prevention, treatment and alleviation of symptoms of the above mentioned diseases.
Currently, much attention is paid to Cannabis derivatives-phytocannabinoids, which interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) constituents. Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are the most abundant compounds of Cannabis plants and their therapeutic application has been suggested. CBD is considered as a potential therapeutic agent due to its anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-tumor, neuroprotective, and potential anti-obesity properties. Therefore, in this review, we especially highlight pharmacological properties of CBD as well as its impact on obesity in different tissues.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32194509
“A well-known ancient plant Cannabis sativa has been a subject of scientific interest for over 50 years. Moreover, it has been used for recreational and medical purposes for thousands of years. The plant comprises about 100 phytocannabinoids, which are C21 terpenophenolic constituents. Nowadays, the most-studied phytocannabinoids are: Δ9– tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (Δ9-THCV), cannabinol (CBN), cannabidiol (CBD), cannabidivarin (CBDV), cannabigerol (CBG), and cannabichromene (CBC). So far, many studies have shown therapeutic properties of the above mentioned Cannabis compounds. Therefore, the aim of the current review is to focus on the emerging potential of CBD and other phytocannabinoids, which act as novel therapeutic agents in obesity treatment. From the existing data, we can conclude that CBD has the promising potential as a therapeutic agent and might be effective in alleviating the symptoms of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2020.00114/full

 “Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway with loss of substantia nigra pars compacta neurons and dopamine depletion. Various natural compounds showed protective actions against PD.
“Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway with loss of substantia nigra pars compacta neurons and dopamine depletion. Various natural compounds showed protective actions against PD. “Preclinical and clinical data indicate that
“Preclinical and clinical data indicate that 
 “Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most frequent and aggressive malignant brain tumour, with a poor prognosis despite available surgical and radio-chemotherapy, rising the necessity for searching alternative therapies. Several preclinical studies evaluating the efficacy of
“Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most frequent and aggressive malignant brain tumour, with a poor prognosis despite available surgical and radio-chemotherapy, rising the necessity for searching alternative therapies. Several preclinical studies evaluating the efficacy of  “Cannabis has been considered as a therapeutic strategy to control intractable epilepsy.
“Cannabis has been considered as a therapeutic strategy to control intractable epilepsy. “The
“The  “Phytocannabinoids (pCBs) are a large family of meroterpenoids isolated from the plant Cannabis sativa. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are the best investigated phytocannabinoids due to their relative abundance and interesting bioactivity profiles. In addition to various targets, THC and CBD are also well-known agonists of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), a nuclear receptor involved in energy homeostasis and lipid metabolism. In the search of new pCBs potentially acting as PPARγ agonists, we identified cannabimovone (CBM), a structurally unique abeo-menthane pCB, as a novel PPARγ modulator via a combined computational and experimental approach. The ability of CBM to act as dual PPARγ/α agonist was also evaluated. Computational studies suggested a different binding mode toward the two isoforms, with the compound able to recapitulate the pattern of H-bonds of a canonical agonist only in the case of PPARγ. Luciferase assays confirmed the computational results, showing a selective activation of PPARγ by CBM in the low micromolar range. CBM promoted the expression of PPARγ target genes regulating the adipocyte differentiation and prevented palmitate-induced insulin signaling impairment. Altogether, these results candidate CBM as a novel bioactive compound potentially useful for the treatment of insulin resistance-related disorders.”
“Phytocannabinoids (pCBs) are a large family of meroterpenoids isolated from the plant Cannabis sativa. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are the best investigated phytocannabinoids due to their relative abundance and interesting bioactivity profiles. In addition to various targets, THC and CBD are also well-known agonists of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), a nuclear receptor involved in energy homeostasis and lipid metabolism. In the search of new pCBs potentially acting as PPARγ agonists, we identified cannabimovone (CBM), a structurally unique abeo-menthane pCB, as a novel PPARγ modulator via a combined computational and experimental approach. The ability of CBM to act as dual PPARγ/α agonist was also evaluated. Computational studies suggested a different binding mode toward the two isoforms, with the compound able to recapitulate the pattern of H-bonds of a canonical agonist only in the case of PPARγ. Luciferase assays confirmed the computational results, showing a selective activation of PPARγ by CBM in the low micromolar range. CBM promoted the expression of PPARγ target genes regulating the adipocyte differentiation and prevented palmitate-induced insulin signaling impairment. Altogether, these results candidate CBM as a novel bioactive compound potentially useful for the treatment of insulin resistance-related disorders.”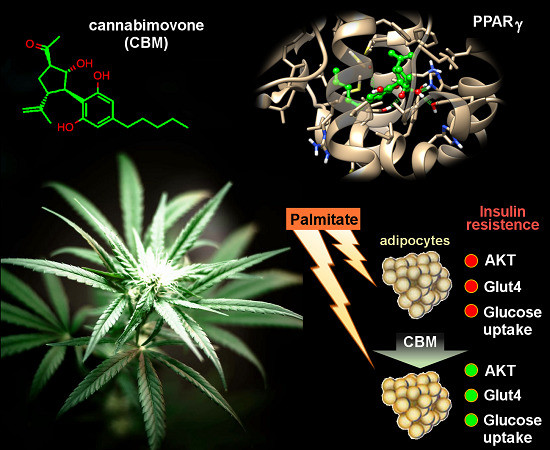
 “Cannabinoids are extracted from Cannabis sativa L. and are used for a variety of medicinal purposes.
“Cannabinoids are extracted from Cannabis sativa L. and are used for a variety of medicinal purposes. “Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by dysregulated keratinocyte differentiation, but oxidative stress also plays an important role in the pathogenesis of this disease.
“Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by dysregulated keratinocyte differentiation, but oxidative stress also plays an important role in the pathogenesis of this disease.