 “The study documented here was aimed to find the molecular interactions of some of the cannabinoid constituents of cannabis with acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Molecular docking and LogP determination were performed to predict the AChE inhibitory effect and lipophilicity. AChE enzyme activity was measured in the blood of cannabis addicted human subjects. Further, genetic predisposition to cannabis addiction was investigated by association analysis of cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1) single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs806368 and ACHE rs17228602 using restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method. All the understudied cannabis constituents showed promising binding affinities with AChE and are lipophilic in nature. The AChE activity was observed to be indifferent in cannabis addicted and non-addicted healthy controls. There was no significant association with CNR1 SNP rs806368 and ACHE rs17228602. The study concludes that in silico prediction for individual biomolecules of cannabis is different from in vivo physiological action in human subjects when all are present together. However, for a deeper mechanistic insight into these interactions and association, multi-population studies are suggested. Further studies to explore the inhibitory potential of different cannabis constituents for intended AChE inhibitor-based drug are warranted.”
“The study documented here was aimed to find the molecular interactions of some of the cannabinoid constituents of cannabis with acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Molecular docking and LogP determination were performed to predict the AChE inhibitory effect and lipophilicity. AChE enzyme activity was measured in the blood of cannabis addicted human subjects. Further, genetic predisposition to cannabis addiction was investigated by association analysis of cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1) single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs806368 and ACHE rs17228602 using restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method. All the understudied cannabis constituents showed promising binding affinities with AChE and are lipophilic in nature. The AChE activity was observed to be indifferent in cannabis addicted and non-addicted healthy controls. There was no significant association with CNR1 SNP rs806368 and ACHE rs17228602. The study concludes that in silico prediction for individual biomolecules of cannabis is different from in vivo physiological action in human subjects when all are present together. However, for a deeper mechanistic insight into these interactions and association, multi-population studies are suggested. Further studies to explore the inhibitory potential of different cannabis constituents for intended AChE inhibitor-based drug are warranted.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32414087
https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/10/5/758


 “There is increasing interest in the use of purified
“There is increasing interest in the use of purified 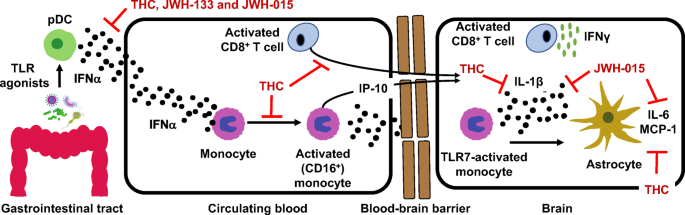
 “Opioid prescriptions and abuse remain a significant national concern.
“Opioid prescriptions and abuse remain a significant national concern. “Modern day research, in an attempt to determine the potential therapeutic and adverse effects of illicit substances, is a growing field, but one that faces many regulatory challenges. Due to the potential abuse of illicit substances such as
“Modern day research, in an attempt to determine the potential therapeutic and adverse effects of illicit substances, is a growing field, but one that faces many regulatory challenges. Due to the potential abuse of illicit substances such as 
.jpg) “Despite limited data demonstrating pronounced negative effects of prenatal cannabis exposure, popular opinion and public policies still reflect the belief that cannabis is fetotoxic.
“Despite limited data demonstrating pronounced negative effects of prenatal cannabis exposure, popular opinion and public policies still reflect the belief that cannabis is fetotoxic. “An emerging area of preclinical research has investigated whether drug use in parents prior to conception influences drug responsivity in their offspring.
“An emerging area of preclinical research has investigated whether drug use in parents prior to conception influences drug responsivity in their offspring. “Cannabis sativa and its principal components, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and
“Cannabis sativa and its principal components, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and