“In the recent years, the application of new antitumor drugs has focused on the replacement of conventional chemotherapeutics with compounds derived from natural products.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the 113 cannabinoids derived from the plant Cannabis sativa and is characterized with complex and not entirely understood biological function. Unlike the other most abundant cannabinoid in Cannabis sativa – tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol has low affinity to the endocannabinoid receptors and the manifestation of its activity does not appear to rely on the endocannabinoid system.
Cannabidiol is used in the treatment of many diseases including some types of cancer.
The aim of our study was to evaluate the cytotoxic activity of cannabidiol and its effect on the process of programmed cell death. This process is directly involved in the antitumor effect of many drugs.
We found that CBD treatment led to a dose-dependant apoptosis increase in p53 positive A549 cells.
Several studies have demonstrated that cannabinoids also have antineoplastic effect and are usually accompanied with no negative side effects such as the ones produced by the conventional chemotherapy treatment.”
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13102818.2021.1915870

 “The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.
“The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.  “Cannabidiol (CBD), the major non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis, is frequently used both as a nutraceutical and therapeutic.
“Cannabidiol (CBD), the major non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis, is frequently used both as a nutraceutical and therapeutic.  “Clinical and preclinical evidence has indicated that estrogen depletion leads to memory impairments and increases the susceptibility to neural damage.
“Clinical and preclinical evidence has indicated that estrogen depletion leads to memory impairments and increases the susceptibility to neural damage.  “Persistent inflammation occurs in people with HIV (PWH) and has many downstream adverse effects including myocardial infarction, neurocognitive impairment and death.
“Persistent inflammation occurs in people with HIV (PWH) and has many downstream adverse effects including myocardial infarction, neurocognitive impairment and death. “The liver is a key metabolic organ that is particularly sensitive to environmental factors, including UV radiation. As UV radiation induces oxidative stress and inflammation, natural compounds are under investigation as one method to counteract these consequences.
“The liver is a key metabolic organ that is particularly sensitive to environmental factors, including UV radiation. As UV radiation induces oxidative stress and inflammation, natural compounds are under investigation as one method to counteract these consequences.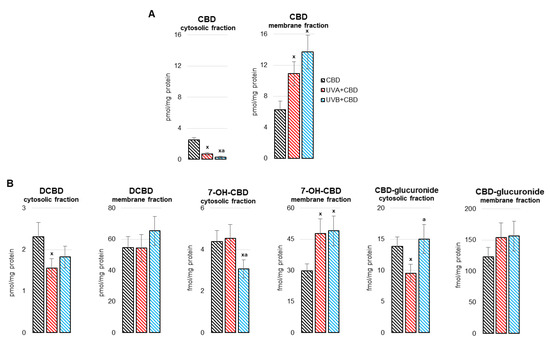
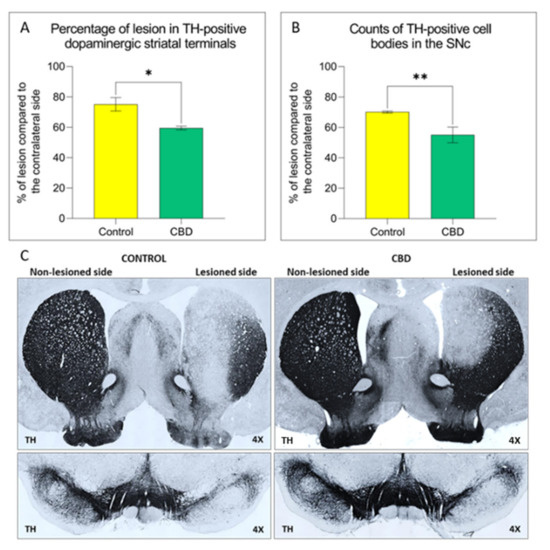
 “Obesity-related insulin resistance (IR) and attenuated brain insulin signaling are significant risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders, e.g., Alzheimer’s disease. IR and type 2 diabetes correlate with an increased concentration of sphingolipids, a class of lipids that play an essential structural role in cellular membranes and cell signaling pathways.
“Obesity-related insulin resistance (IR) and attenuated brain insulin signaling are significant risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders, e.g., Alzheimer’s disease. IR and type 2 diabetes correlate with an increased concentration of sphingolipids, a class of lipids that play an essential structural role in cellular membranes and cell signaling pathways. “Cannabidiol is increasingly considered for treatment of a wide range of medical conditions.
“Cannabidiol is increasingly considered for treatment of a wide range of medical conditions.