 “Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g., cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) agonists including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
“Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g., cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) agonists including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
The combined use of THC and CBD confers greater benefits, as CBD enhances the effects of THC and reduces its psychotropic activity. We assessed the relationship between the expression levels of CB1 and CB2 to the clinical features of a cohort of patients with NSCLC, and the effect of THC and CBD (individually and in combination) on proliferation, EMT and migration in vitro in A549, H460 and H1792 lung cancer cell lines.
METHODS:
Expression levels of CB1, CB2, EGFR, CDH1, CDH2 and VIM were evaluated by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. THC and CBD (10-100 μM), individually or in combination (1:1 ratio), were used for in vitro assays. Cell proliferation was determined by BrdU incorporation assay. Morphological changes in the cells were visualized by phase-contrast and fluorescence microscopy. Migration was studied by scratch recolonization induced by 20 ng/ml epidermal growth factor (EGF).
RESULTS:
The tumor samples were classified according to the level of expression of CB1, CB2, or both. Patients with high expression levels of CB1, CB2, and CB1/CB2 showed increased survival reaching significance for CB1 and CB1/CB2 (p = 0.035 and 0.025, respectively).
Both cannabinoid agonists inhibited the proliferation and expression of EGFR in lung cancer cells, and CBD potentiated the effect of THC. THC and CBD alone or in combination restored the epithelial phenotype, as evidenced by increased expression of CDH1 and reduced expression of CDH2 and VIM, as well as by fluorescence analysis of cellular cytoskeleton.
Finally, both cannabinoids reduced the in vitro migration of the three lung cancer cells lines used.
CONCLUSIONS:
The expression levels of CB1 and CB2 have a potential use as markers of survival in patients with NSCLC. THC and CBD inhibited the proliferation and expression of EGFR in the lung cancer cells studied. Finally, the THC/CBD combination restored the epithelial phenotype in vitro.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32049991
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0228909

 “Plant phytochemicals have potential decontaminating properties, however, their role in the amelioration of hydrophobic water filtration membranes have not been elucidated yet.
“Plant phytochemicals have potential decontaminating properties, however, their role in the amelioration of hydrophobic water filtration membranes have not been elucidated yet.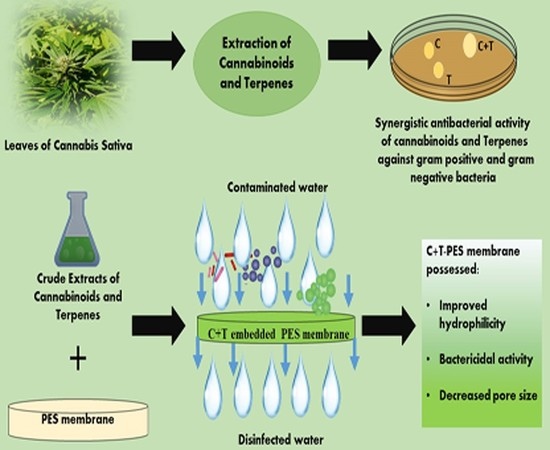
 “Novel anticancer medicines, including targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, have greatly improved the management of cancers. However, both conventional and new anticancer treatments induce cardiac adverse effects, which remain a critical issue in clinic.
“Novel anticancer medicines, including targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, have greatly improved the management of cancers. However, both conventional and new anticancer treatments induce cardiac adverse effects, which remain a critical issue in clinic. “Sleep deprivation (SD) is a common feature in modern society. Prolonged sleep deprivation causes cognition deficits and depression-like behavior in the model of animal experiments.
“Sleep deprivation (SD) is a common feature in modern society. Prolonged sleep deprivation causes cognition deficits and depression-like behavior in the model of animal experiments. “The rationale of this study was to assess occurrence of withdrawal symptoms induced by abrupt cessation of cannabidiol (CBD) after prolonged administration in healthy volunteers.
“The rationale of this study was to assess occurrence of withdrawal symptoms induced by abrupt cessation of cannabidiol (CBD) after prolonged administration in healthy volunteers. “Most of the drugs of abuse affect the brain by interacting with naturally expressed molecular receptors. Marihuana affects a series of receptors including
“Most of the drugs of abuse affect the brain by interacting with naturally expressed molecular receptors. Marihuana affects a series of receptors including  “The use of medical cannabis in children is rapidly growing.
“The use of medical cannabis in children is rapidly growing.