 “Industrial hemp is a multiuse crop that has been widely cultivated to produce fibers and nutrients. The capability of the essential oil (EO) from inflorescences as antimicrobial agent has been reported. However, literature data are still lacking about the hemp EO antiprotozoal efficacy in vivo.
“Industrial hemp is a multiuse crop that has been widely cultivated to produce fibers and nutrients. The capability of the essential oil (EO) from inflorescences as antimicrobial agent has been reported. However, literature data are still lacking about the hemp EO antiprotozoal efficacy in vivo.
The present study aims to unravel this concern through the evaluation of the efficacy of hemp EOs (2.5 mL/kg, intraperitoneally) of three different cultivars, namely Futura 75, Carmagnola selezionata and Eletta campana, in mice intraperitoneally infected with Leishmania tropica. A detailed description of EO composition and targets-components analysis is reported.
Myrcene, α-pinene and E-caryophyllene were the main components of the EOs, as indicated by the gas-chromatographic analysis. However, a prominent position in the scenario of the theoretical interactions underlying the bio-pharmacological activity was also occupied by selina-3,7(11)-diene, which displayed affinities in the micromolar range (5.4-28.9) towards proliferator-activated receptor α, cannabinoid CB2 receptor and acetylcholinesterase. The content of this compound was higher in Futura 75 and Eletta campana, in accordance with their higher scavenging/reducing properties and efficacy against the tissue wound, induced by L. tropica.
Overall, the present study recommends hemp female inflorescences, as sources of biomolecules with potential pharmacological applications, especially towards infective diseases.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33673274/
https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/11/2/272

 “(E)-β-caryophyllene (BCP) is a bicyclic sesquiterpene widely distributed in the plant kingdom, where it contributes a unique aroma to essential oils and has a pivotal role in the survival and evolution of higher plants.
“(E)-β-caryophyllene (BCP) is a bicyclic sesquiterpene widely distributed in the plant kingdom, where it contributes a unique aroma to essential oils and has a pivotal role in the survival and evolution of higher plants. “Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed contains high contents of various nutrients, including fatty acids and proteins.
“Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed contains high contents of various nutrients, including fatty acids and proteins.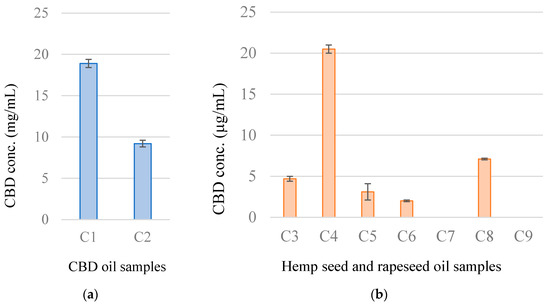
 “Hemp (Cannabis sativa) is an angiosperm plant belonging to the Cannabaceae family. Its cultivation dates back to centuries. It has always been cultivated due to the possibility of exploiting almost all the parts of the plant: paper, fabrics, ropes, bio-compounds with excellent insulating capacity, fuel, biodegradable plastic, antibacterial detergents, and food products, such as flour, oils, seeds, herbal teas, and beer, are indeed obtained from hemp.
“Hemp (Cannabis sativa) is an angiosperm plant belonging to the Cannabaceae family. Its cultivation dates back to centuries. It has always been cultivated due to the possibility of exploiting almost all the parts of the plant: paper, fabrics, ropes, bio-compounds with excellent insulating capacity, fuel, biodegradable plastic, antibacterial detergents, and food products, such as flour, oils, seeds, herbal teas, and beer, are indeed obtained from hemp.





