“Extracts from the cannabis plant can dramatically improve the health of children suffering from refractory epilepsies such as Dravet syndrome.
“Extracts from the cannabis plant can dramatically improve the health of children suffering from refractory epilepsies such as Dravet syndrome.
These extracts typically contain cannabidiol (CBD), a phytocannabinoid with well-documented anticonvulsant effects, but may also contain Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9 -THC). It is unclear whether the presence of Δ9 -THC modulates the anticonvulsant efficacy of CBD. Here we utilized the Scn1a+/- mouse model of Dravet syndrome to examine this question.
Key results: Administered alone, CBD (100 mg/kg i.p.) was anticonvulsant against hyperthermia-induced seizures as were low (0.1 and 0.3 mg/kg i.p.) but not higher doses of Δ9 -THC. A subthreshold dose of CBD (12 mg/kg) enhanced the anticonvulsant effects Δ9 -THC (0.1 mg/kg). Subchronic oral administration of Δ9 -THC or CBD alone did not affect spontaneous seizure frequency or mortality while, surprisingly, their co-administration increased the severity of spontaneous seizures and overall mortality.
Conclusion and implications: Low doses of Δ9 -THC are anticonvulsant against hyperthermia-induced seizures in Scn1a+/ mice, effects that are enhanced by a sub-anticonvulsant dose of CBD. However, proconvulsant effects and increased premature mortality are observed when CBD and Δ9 -THC are subchronically dosed in combination. The possible explanations and implications of this are discussed.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32608111/
https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/bph.15181

 “The Cannabis plant contains numerous components, including cannabinoids and other active molecules. The phyto-cannabinoid activity is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Cannabinoids affect the nervous system and play significant roles in the regulation of the immune system.
“The Cannabis plant contains numerous components, including cannabinoids and other active molecules. The phyto-cannabinoid activity is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Cannabinoids affect the nervous system and play significant roles in the regulation of the immune system.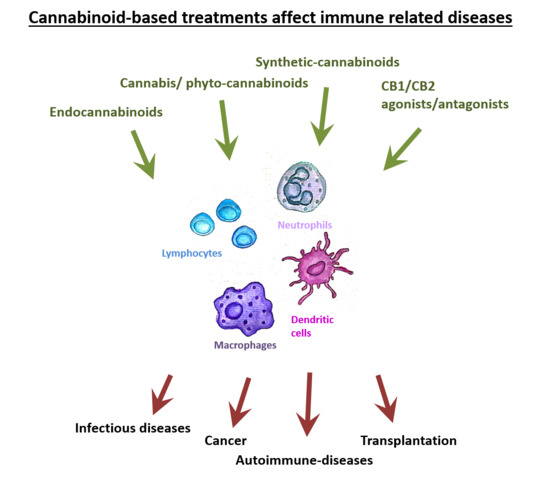
 “Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical
“Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical  “The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB/Akt)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway has been associated with several pathologies in the central nervous system (CNS), including epilepsy. There is evidence supporting the hypothesis that the PI3Kγ signaling pathway may mediate the powerful anticonvulsant properties associated with the cannabinoidergic system.
“The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (PKB/Akt)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway has been associated with several pathologies in the central nervous system (CNS), including epilepsy. There is evidence supporting the hypothesis that the PI3Kγ signaling pathway may mediate the powerful anticonvulsant properties associated with the cannabinoidergic system.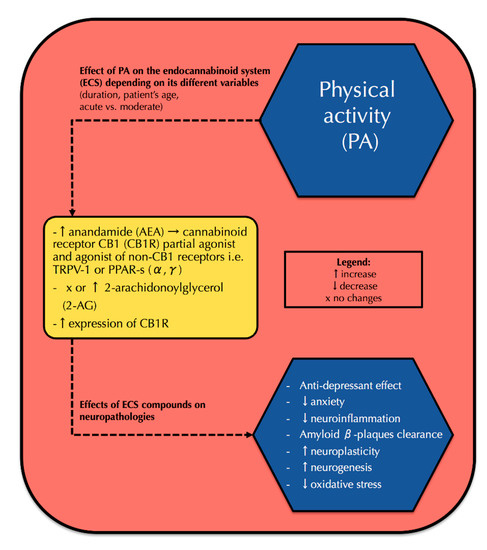
 “Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is currently the most rapid growing neurodegenerative disease and over the past generation, its global burden has more than doubled. The onset of PD can arise due to environmental, sporadic or genetic factors. Nevertheless, most PD cases have an unknown etiology.
“Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is currently the most rapid growing neurodegenerative disease and over the past generation, its global burden has more than doubled. The onset of PD can arise due to environmental, sporadic or genetic factors. Nevertheless, most PD cases have an unknown etiology. “Medical cannabis (MC) treatment for migraine is practically emerging, although sufficient clinical data are not available for this indication. This cross-sectional questionnaire-based study aimed to investigate the associations between phytocannabinoid treatment and migraine frequency.
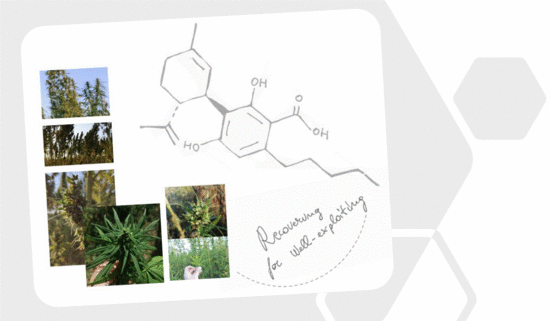
“Medical cannabis (MC) treatment for migraine is practically emerging, although sufficient clinical data are not available for this indication. This cross-sectional questionnaire-based study aimed to investigate the associations between phytocannabinoid treatment and migraine frequency. “Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) is the main phytocannabinoid in fiber and seed-oil hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) plants, but its potential health-related capabilities have been masked for years by a greater scientific interest towards its neutral derivative cannabidiol (CBD). This review aims to collect from the literature and critically discuss all the information about this molecule, starting from its biosynthesis, and focusing on its bioactivity, as an anti-inflammatory, anti-emetic, anti-convulsant, and anti-cancerogenic drug. Furthermore, in the awareness that, despite its multiple bioactive effects, currently poor efforts have been made to achieve its reliable purification, herein, we propose a relatively simple, fast, and inexpensive procedure for its recovery from pollen of industrial hemp cultivars. Spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques allowed us to unequivocally identify pure isolated CBDA and to distinguish it from the constitutional isomer tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA-A).”
“Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) is the main phytocannabinoid in fiber and seed-oil hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) plants, but its potential health-related capabilities have been masked for years by a greater scientific interest towards its neutral derivative cannabidiol (CBD). This review aims to collect from the literature and critically discuss all the information about this molecule, starting from its biosynthesis, and focusing on its bioactivity, as an anti-inflammatory, anti-emetic, anti-convulsant, and anti-cancerogenic drug. Furthermore, in the awareness that, despite its multiple bioactive effects, currently poor efforts have been made to achieve its reliable purification, herein, we propose a relatively simple, fast, and inexpensive procedure for its recovery from pollen of industrial hemp cultivars. Spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques allowed us to unequivocally identify pure isolated CBDA and to distinguish it from the constitutional isomer tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA-A).”