“Cannabis contains a multitude of different compounds. One of them, cannabidiol – a non-psychoactive substance – might counteract negative effects of Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol on hippocampus-dependent memory impairment.
“Cannabis contains a multitude of different compounds. One of them, cannabidiol – a non-psychoactive substance – might counteract negative effects of Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol on hippocampus-dependent memory impairment.
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of vaping cannabidiol on verbal episodic memory in healthy young subjects.
We used a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized crossover trial in 39 healthy young subjects. Participants received once a single dose of cannabidiol e-liquid (0.25 ml, 5% cannabidiol, 12.5 mg cannabidiol) and once placebo for vaping after learning 15 unrelated nouns. The primary outcome measure was the short delay verbal memory performance (number of correctly free recalled nouns) 20 min after learning. 34 participants (mean age: 22.26 [3.04]) completed all visits and entered analyses (17 received cannabidiol and 17 received placebo first).
Cannabidiol enhanced verbal episodic memory performance (placebo: 7.03 [2.34]; cannabidiol 7.71 [2.48]; adjusted group difference 0.68, 95% CI 0.01 to 1.35; R2β = .028, p = .048). Importantly, we did not detect medication effects on secondary outcome measures attention or working memory performance, suggesting that CBD has no negative impact on these basic cognitive functions.
The results are in line with the idea that vaping cannabidiol interacts with the central endocannabinoid system and is capable to modulate memory processes, a phenomenon with possible therapeutic potential. Further studies are needed to investigate optimal dose-response and time-response relationships.”
“To conclude, while further research is needed to identify dose-response and time-response relationships, our results show that CBD can improve episodic memory, a drug effect with possible therapeutic potential.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002239562100546X?via%3Dihub

 “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating phytocannabinoid whose purported therapeutic benefits and impression of a high safety profile has promoted its increasing popularity.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating phytocannabinoid whose purported therapeutic benefits and impression of a high safety profile has promoted its increasing popularity. “The possible evolutionary trend of COVID-19 in South Africa was investigated by comparing the genome of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from a patient in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa with those isolated from China, Spain, Italy, and United States, as well as the genomes of Bat SARS CoV, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), Mouse Hepatitis Virus (MHV), and Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV). Phylogenetic analysis revealed a strong homology (96%) between the genomes of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa and those isolated from the study countries as well as those isolated from bat SARS CoV, MERS-CoV, MHV and IBV.
“The possible evolutionary trend of COVID-19 in South Africa was investigated by comparing the genome of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from a patient in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa with those isolated from China, Spain, Italy, and United States, as well as the genomes of Bat SARS CoV, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), Mouse Hepatitis Virus (MHV), and Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV). Phylogenetic analysis revealed a strong homology (96%) between the genomes of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa and those isolated from the study countries as well as those isolated from bat SARS CoV, MERS-CoV, MHV and IBV.  “Cannabidiol (CBD), a primary bioactive phytocannabinoid extracted from hemp, is reported to possess potent anti-tumorigenic activity in multiple cancers.
“Cannabidiol (CBD), a primary bioactive phytocannabinoid extracted from hemp, is reported to possess potent anti-tumorigenic activity in multiple cancers.  “Cannabinoids, active components of the plant
“Cannabinoids, active components of the plant  “Cannabidiol (CBD), the major non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis, is frequently used both as a nutraceutical and therapeutic.
“Cannabidiol (CBD), the major non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis, is frequently used both as a nutraceutical and therapeutic.  “Clinical and preclinical evidence has indicated that estrogen depletion leads to memory impairments and increases the susceptibility to neural damage.
“Clinical and preclinical evidence has indicated that estrogen depletion leads to memory impairments and increases the susceptibility to neural damage.  “In the study, we assessed the effect of hemp extract on activities of resistance parameters and the metabolic compound concentration in adult workers’ hemolymph. Bees were divided into the following groups: (1) control group fed with mixture of sugar and water-glycerine solution, (2) experimental group with pure sugar syrup and inside with cotton strips soaked with hemp extract, (3) experimental group with a mixture of sugar syrup with hemp extract. Hemp extracts caused an increase in the protein concentrations and reduced the protease activities regardless of the administration method. The protease inhibitor activities were decreased only in the group that received hemp extract on the strips. The biomarker activities (ALP, ALT, AST) increased from the control group and workers feeding extract in syrup and decreased in workers supplemented with the extract on strips. In young, 2-day-old workers, the glucose concentration was higher in the groups feeding with the extract than in the control. Hemp extract influenced an increase in urea concentrations in workers’ hemolymph in comparison with the control. The hemp supplementation positively influences the immune system of workers, and the appropriate method of administration may be adapted to the health problems of bees.”
“In the study, we assessed the effect of hemp extract on activities of resistance parameters and the metabolic compound concentration in adult workers’ hemolymph. Bees were divided into the following groups: (1) control group fed with mixture of sugar and water-glycerine solution, (2) experimental group with pure sugar syrup and inside with cotton strips soaked with hemp extract, (3) experimental group with a mixture of sugar syrup with hemp extract. Hemp extracts caused an increase in the protein concentrations and reduced the protease activities regardless of the administration method. The protease inhibitor activities were decreased only in the group that received hemp extract on the strips. The biomarker activities (ALP, ALT, AST) increased from the control group and workers feeding extract in syrup and decreased in workers supplemented with the extract on strips. In young, 2-day-old workers, the glucose concentration was higher in the groups feeding with the extract than in the control. Hemp extract influenced an increase in urea concentrations in workers’ hemolymph in comparison with the control. The hemp supplementation positively influences the immune system of workers, and the appropriate method of administration may be adapted to the health problems of bees.” “The liver is a key metabolic organ that is particularly sensitive to environmental factors, including UV radiation. As UV radiation induces oxidative stress and inflammation, natural compounds are under investigation as one method to counteract these consequences.
“The liver is a key metabolic organ that is particularly sensitive to environmental factors, including UV radiation. As UV radiation induces oxidative stress and inflammation, natural compounds are under investigation as one method to counteract these consequences.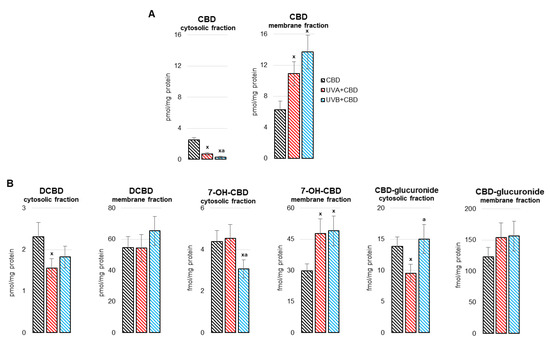
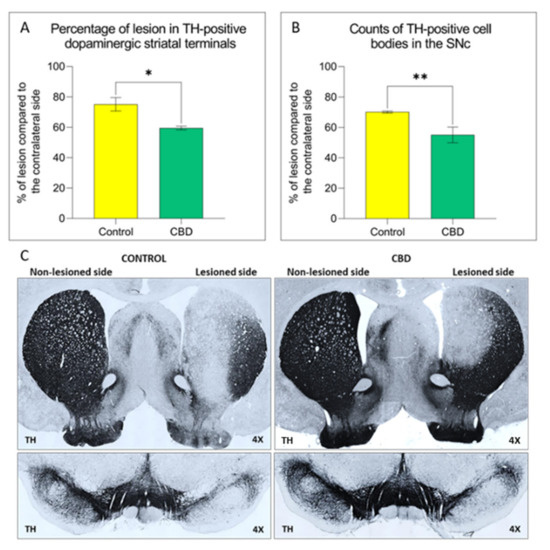
 “Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the Substantia Nigra pars compacta, leading to classical PD motor symptoms. Current therapies are purely symptomatic and do not modify disease progression.
“Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the Substantia Nigra pars compacta, leading to classical PD motor symptoms. Current therapies are purely symptomatic and do not modify disease progression.