“In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids.
“In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids.
Several lines of evidence suggest that the ECS plays a complex role in cardiac and vascular systems; however, under normal physiological conditions the functions of the ECS are limited. Overactivation of components of the ECS has been associated with various cardiovascular conditions.
Intriguingly, activation of the ECS may also reflect a cardioprotective compensatory mechanism. With this knowledge, a range of naturally occurring and synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists and antagonists, as well as inhibitors of endocannabinoid metabolic enzymes have emerged as promising approaches for the treatment or management of cardiovascular health.
This review will first focus on the known role of the ECS in regulating the cardiovascular system. Secondly, we discuss emerging data highlighting the therapeutic potential of naturally occurring non-psychoactive ECS modulators within the cardiovascular system, including phytocannabinoids, terpenes, and the endocannabinoid-like molecule palmitoylethanolamide.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32677481/
“Several approaches discussed here, including administration of eCB-related molecules such as PEA, or supplementing with various phytocannabinoids can be promising candidates for the management of cardiovascular risk factors and CVD.”
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19390211.2020.1790708



 “Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) has become widely used in several sectors due to the presence of various bioactive compounds such as terpenes and
“Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) has become widely used in several sectors due to the presence of various bioactive compounds such as terpenes and  “The aim of this study was to compare the micro-morphological features of two different non-drug
“The aim of this study was to compare the micro-morphological features of two different non-drug  “Cannabis sativa or Indian hemp (subfamily Cannaboideae of family Moraceae) is an annual herbaceous plant, native to central and western Asia, cultivated for medicinal properties and for hemp, which is a natural textile fiber. The plant contains over 400 chemical compounds, of which approximately 80 biologically active chemical molecules. The most important cannabis compounds are cannabinoids formed by a terpene combined with resorcinol, or, according to a different nomenclature, by a benzopyranic ring system. There are about sixty cannabinoids, of which the most important psychoactive compound is tetrahydrocannabinol (TCH), in particular the isomer delta (Δ9-THC). Other identified compounds are
“Cannabis sativa or Indian hemp (subfamily Cannaboideae of family Moraceae) is an annual herbaceous plant, native to central and western Asia, cultivated for medicinal properties and for hemp, which is a natural textile fiber. The plant contains over 400 chemical compounds, of which approximately 80 biologically active chemical molecules. The most important cannabis compounds are cannabinoids formed by a terpene combined with resorcinol, or, according to a different nomenclature, by a benzopyranic ring system. There are about sixty cannabinoids, of which the most important psychoactive compound is tetrahydrocannabinol (TCH), in particular the isomer delta (Δ9-THC). Other identified compounds are  “Cannabis sativa produces hundreds of phytocannabinoids and terpenes.
“Cannabis sativa produces hundreds of phytocannabinoids and terpenes. “Cannabis has been used for thousands of years in many cultures for the treatment of several ailments including pain.
“Cannabis has been used for thousands of years in many cultures for the treatment of several ailments including pain. “Cannabis sativa L. (C. sativa) contains an array of plant-derived (phyto)
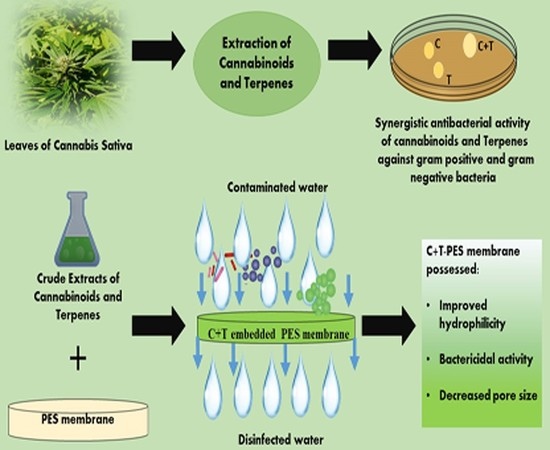
“Cannabis sativa L. (C. sativa) contains an array of plant-derived (phyto)  “Plant phytochemicals have potential decontaminating properties, however, their role in the amelioration of hydrophobic water filtration membranes have not been elucidated yet.
“Plant phytochemicals have potential decontaminating properties, however, their role in the amelioration of hydrophobic water filtration membranes have not been elucidated yet.