“Decline in cognitive performance, an aspect of the normal aging process, is influenced by the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) signaling diminishes with advancing age in specific brain regions that regulate learning and memory and abolishing CB1 receptor signaling accelerates cognitive aging in mice.
“Decline in cognitive performance, an aspect of the normal aging process, is influenced by the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) signaling diminishes with advancing age in specific brain regions that regulate learning and memory and abolishing CB1 receptor signaling accelerates cognitive aging in mice.
We recently demonstrated that prolonged exposure to low dose (3 mg/kg/day) Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) improved the cognitive performances in old mice on par with young untreated mice. Here we investigated the potential influence of cannabidiol (CBD) on this THC effect, because preclinical and clinical studies indicate that the combination of THC and CBD often exhibits an enhanced therapeutic effect compared to THC alone.
We first tested the effectiveness of a lower dose (1 mg/kg/day) THC, and then the efficacy of the combination of THC and CBD in 1:1 ratio, same as in the clinically approved medicine Sativex®. Our findings reveal that a 1 mg/kg/day THC dose still effectively improved spatial learning in aged mice. However, a 1:1 combination of THC and CBD failed to do so.
The presence of CBD induced temporal changes in THC metabolism ensuing in a transient elevation of blood THC levels. However, as CBD metabolizes, the inhibitory effect on THC metabolism was alleviated, causing a rapid clearance of THC. Thus, the beneficial effects of THC seemed to wane off more swiftly in the presence of CBD, due to these metabolic effects.
The findings indicate that THC-treatment alone is more efficient to improve spatial learning in aged mice than the 1:1 combination of THC and CBD.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34526890/
“In conclusion, our observations indicate that 1 mg/kg/day THC dose is still effective in improving the spatial learning in aged mice. With regard to the efficacy, THC-alone has proved to be more efficient in improving spatial learning in aged mice than its 1:1 combination with CBD. However, the possibility of THC/CBD being efficient in other ratios or at the earliest time-points, like immediately after the treatment cease, cannot be negated. Possibly, reducing the dose of CBD may improve the efficacy of the THC/CBD combination.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2021.718850/full

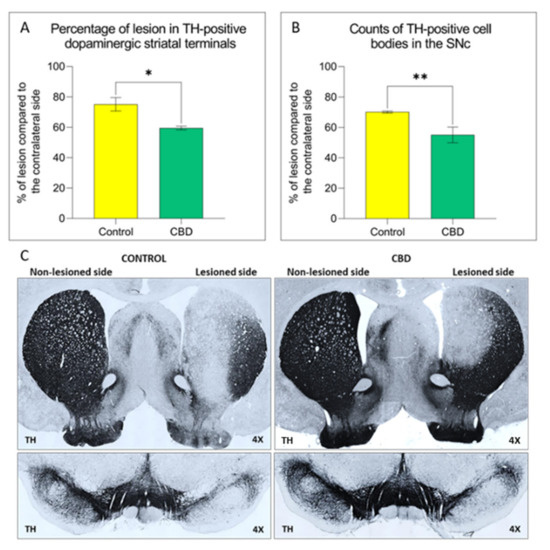
 “Cannabis contains a multitude of different compounds. One of them, cannabidiol – a non-psychoactive substance – might counteract negative effects of Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol on hippocampus-dependent memory impairment.
“Cannabis contains a multitude of different compounds. One of them, cannabidiol – a non-psychoactive substance – might counteract negative effects of Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol on hippocampus-dependent memory impairment.  “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating phytocannabinoid whose purported therapeutic benefits and impression of a high safety profile has promoted its increasing popularity.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating phytocannabinoid whose purported therapeutic benefits and impression of a high safety profile has promoted its increasing popularity. “The possible evolutionary trend of COVID-19 in South Africa was investigated by comparing the genome of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from a patient in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa with those isolated from China, Spain, Italy, and United States, as well as the genomes of Bat SARS CoV, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), Mouse Hepatitis Virus (MHV), and Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV). Phylogenetic analysis revealed a strong homology (96%) between the genomes of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa and those isolated from the study countries as well as those isolated from bat SARS CoV, MERS-CoV, MHV and IBV.
“The possible evolutionary trend of COVID-19 in South Africa was investigated by comparing the genome of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from a patient in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa with those isolated from China, Spain, Italy, and United States, as well as the genomes of Bat SARS CoV, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), Mouse Hepatitis Virus (MHV), and Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV). Phylogenetic analysis revealed a strong homology (96%) between the genomes of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa and those isolated from the study countries as well as those isolated from bat SARS CoV, MERS-CoV, MHV and IBV.  “”Medicinal cannabis” is defined as the use of cannabis-based products for the treatment of an illness. Investigations of cannabis compounds in psychiatric and neurological illnesses primarily focus on the major cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ
“”Medicinal cannabis” is defined as the use of cannabis-based products for the treatment of an illness. Investigations of cannabis compounds in psychiatric and neurological illnesses primarily focus on the major cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ “Cannabinoids, active components of the plant
“Cannabinoids, active components of the plant 
 “The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.
“The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.  “Cannabidiol (CBD), the major non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis, is frequently used both as a nutraceutical and therapeutic.
“Cannabidiol (CBD), the major non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis, is frequently used both as a nutraceutical and therapeutic.