 “Medicinal cannabis has remarkable therapeutic potential, but its clinical use is limited by the psychotropic activity of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC). However, the biological profile of the carboxylated, non-narcotic native precursor of Δ9-THC, the Δ9-THC acid A (Δ9-THCA-A), remains largely unexplored.
“Medicinal cannabis has remarkable therapeutic potential, but its clinical use is limited by the psychotropic activity of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC). However, the biological profile of the carboxylated, non-narcotic native precursor of Δ9-THC, the Δ9-THC acid A (Δ9-THCA-A), remains largely unexplored.
Here we present evidence that Δ9-THCA-A is a partial and selective PPARγ modulator, endowed with lower adipogenic activity than the full PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone (RGZ) and enhanced osteoblastogenic effects in hMSC. Docking and in vitro functional assays indicated that Δ9-THCA-A binds to and activates PPARγ by acting at both the canonical and the alternative sites of the ligand-binding domain. Transcriptomic signatures in iWAT from mice treated with Δ9-THCA-A confirmed its mode of action through PPARγ.
Administration of Δ9-THCA-A in a mouse model of HFD-induced obesity significantly reduced fat mass and body weight gain, markedly ameliorating glucose intolerance and insulin resistance, and largely preventing liver steatosis, adipogenesis and macrophage infiltration in fat tissues. Additionally, immunohistochemistry, transcriptomic, and plasma biomarker analyses showed that treatment with Δ9-THCA-A caused browning of iWAT and displayed potent anti-inflammatory actions in HFD mice.
Our data validate the potential of Δ9-THCA-A as a low adipogenic PPARγ agonist, capable of substantially improving the symptoms of obesity-associated metabolic syndrome and inflammation.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31706843
“Δ9-THCA-A is a partial PPARγ ligand agonist with low adipogenic activity. Δ9-THCA-A enhances osteoblastogenesis in bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Δ9-THCA-A reduces body weight gain, fat mass, and liver steatosis in HFD-fed mice. Δ9-THCA-A improves glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity, and insulin profiles in vivo. Δ9-THCA-A induces browning of iWAT and has a potent anti-inflammatory activity.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0006295219303922?via%3Dihub

 “Endocannabinoids are produced within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and modulate energy homeostasis and food intake, at least in part, via vagally-dependent actions. The recent paper by Christie et al., [Christie, et al. J Physiol, 2019] demonstrate, for the first time, that
“Endocannabinoids are produced within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and modulate energy homeostasis and food intake, at least in part, via vagally-dependent actions. The recent paper by Christie et al., [Christie, et al. J Physiol, 2019] demonstrate, for the first time, that 

 “According to recent studies,
“According to recent studies, 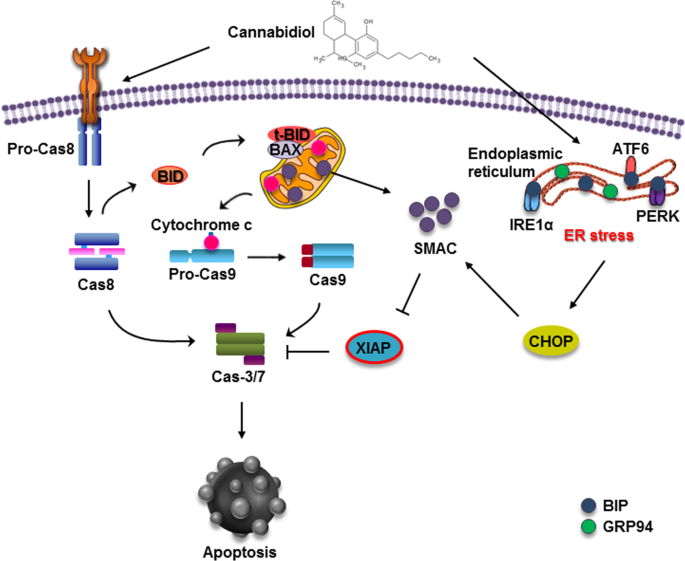
 “Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder classically associated with motor symptoms, but several nonmotor disturbances appear decades before the clinical diagnosis of the disease.
“Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder classically associated with motor symptoms, but several nonmotor disturbances appear decades before the clinical diagnosis of the disease. “Pain is the most frequent indication for which medical
“Pain is the most frequent indication for which medical 

 “The endocannabinoid (eCB) system, i.e. the receptors that respond to the psychoactive component of
“The endocannabinoid (eCB) system, i.e. the receptors that respond to the psychoactive component of  “The anticancer effects of the omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA), EPA and DHA may be due, at least in part, to conversion to their respective endocannabinoid derivatives, eicosapentaenoyl-ethanolamine (EPEA) and docosahexaenoyl-ethanolamine (DHEA).
“The anticancer effects of the omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA), EPA and DHA may be due, at least in part, to conversion to their respective endocannabinoid derivatives, eicosapentaenoyl-ethanolamine (EPEA) and docosahexaenoyl-ethanolamine (DHEA). “Prostate cancer patients receiving androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) often experience a combination of disease symptoms and treatment side effects. The therapeutic use of
“Prostate cancer patients receiving androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) often experience a combination of disease symptoms and treatment side effects. The therapeutic use of