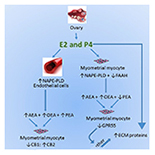
“The aim of this study was to determine if components of the endocannabinoid system are modulated in uterine leiomyomas (fibroids). Components studied included cannabinoid receptors 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2); the G protein-coupled receptor GPR55; transient potential vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) and the endocannabinoid modulating enzymes N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD) and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and their N-acylethanolamine (NAE) ligands: N-arachidonylethanolamine (AEA), N-oleoylethanolamine (OEA), and N-palmityolethanaolamine (PEA). MATERIAL AND METHODS Transcript levels of CB1, CB2, TRPV1, GPR55, NAPE-PLD, and FAAH were measured using RT-PCR and correlated with the tissue levels of the 3 NAEs in myometrial tissues. The tissues studied were: 1) fibroids, 2) myometrium adjacent/juxtaposed to the fibroid lesions, and 3) normal myometrium. Thirty-seven samples were processed for NAE measurements and 28 samples were used for RT-PCR analyses. RESULTS FAAH expression was significantly lower in fibroids, resulting in a NAPE-PLD: FAAH ratio that favors higher AEA levels in pre-menopausal tissues, whilst PEA levels were significantly lower, particularly in post-menopausal women, suggesting PEA protects against fibroid pathogenesis. The CB1: CB2 ratio was lower in fibroids, suggesting that loss of CB1 expression affects the fibroid cell phenotype. Significant correlations between reduced FAAH, CB1, and GPR55 expression and PEA in fibroids indicate that the loss of these endocannabinoid system components are biomarkers of leiomyomata. CONCLUSIONS Loss of expression of CB1, FAAH, GPR55, and PEA production are linked to the pathogenesis of uterine fibroids and further understanding of this might eventually lead to better disease indicators or the development of therapeutic potentials that might eventually be used in the management of uterine fibroids.”

 “Substance use disorder is characterized by repeated use of a substance, leading to clinically significant distress, making it a serious public health concern. The endocannabinoid system plays an important role in common neurobiological processes underlying substance use disorder, in particular by mediating the rewarding and motivational effects of substances and substance-related cues. In turn, a number of
“Substance use disorder is characterized by repeated use of a substance, leading to clinically significant distress, making it a serious public health concern. The endocannabinoid system plays an important role in common neurobiological processes underlying substance use disorder, in particular by mediating the rewarding and motivational effects of substances and substance-related cues. In turn, a number of 






