 “Objective: To determine the benefit of a tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-rich cannabis oil on symptoms and quality of life of fibromyalgia patients.
“Objective: To determine the benefit of a tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)-rich cannabis oil on symptoms and quality of life of fibromyalgia patients.
Conclusions: Phytocannabinoids can be a low-cost and well-tolerated therapy to reduce symptoms and increase the quality of life of patients with fibromyalgia. Future studies are still needed to assess long-term benefits, and studies with different varieties of cannabinoids associated with a washout period must be done to enhance our knowledge of cannabis action in this health condition.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33118602/
“To our knowledge, this is the first randomized controlled trial to demonstrate the benefit of cannabis oil—a THC-rich whole plant extract—on symptoms and on quality of life of people with fibromyalgia. We conclude that phytocannabinoids can be a low-cost and well-tolerated therapy for symptom relief and quality of life improvement in these patients, and we suggest that this therapy could be included as an herbal medicine option for the treatment of this condition”
https://academic.oup.com/painmedicine/article/21/10/2212/5942556

 “The prevalence of cancer pain will continue to rise as pain is common among the survivorship and general cancer population. As interest in cannabis and cannabinoids for medicinal use including pain management continues to rise, there is growing need to update and review the current state of evidence for their use. The literature was searched for articles in English with key words cannabis, cannabinoids, and cancer pain. The sources of articles were PubMed, Embase, and open Google search.
“The prevalence of cancer pain will continue to rise as pain is common among the survivorship and general cancer population. As interest in cannabis and cannabinoids for medicinal use including pain management continues to rise, there is growing need to update and review the current state of evidence for their use. The literature was searched for articles in English with key words cannabis, cannabinoids, and cancer pain. The sources of articles were PubMed, Embase, and open Google search. “In this proof-of-concept study, the antioxidant activity of phytocannabinoids, namely cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), were investigated using an in vitro system of differentiated human neuronal SY-SH5Y cells.
“In this proof-of-concept study, the antioxidant activity of phytocannabinoids, namely cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), were investigated using an in vitro system of differentiated human neuronal SY-SH5Y cells.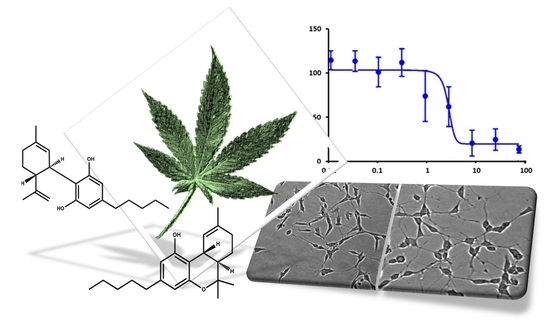
 “Background: Little is known about medical cannabis (MC)-related care for patients with cancer using MC.
“Background: Little is known about medical cannabis (MC)-related care for patients with cancer using MC. “Fish oil (FO) and phytocannabinoids have received considerable attention for their intestinal anti-inflammatory effects.
“Fish oil (FO) and phytocannabinoids have received considerable attention for their intestinal anti-inflammatory effects. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is known for its vasorelaxant (including in the human pulmonary artery), anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of our study was to examine the potential preventive effect of chronic CBD administration (10 mg/kg/day for three weeks) on monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) rats.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is known for its vasorelaxant (including in the human pulmonary artery), anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of our study was to examine the potential preventive effect of chronic CBD administration (10 mg/kg/day for three weeks) on monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) rats.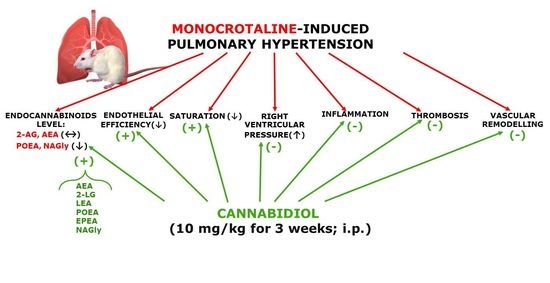
 “Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.
“Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.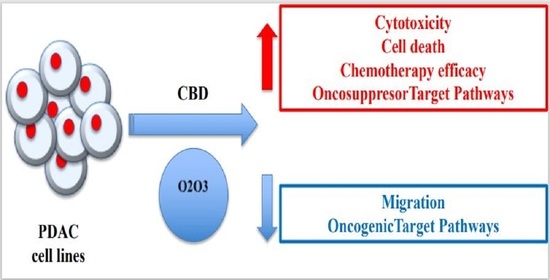
 “In recent years there has been a growing appreciation by regulatory authorities that cannabis-based medicines can play a useful role in disease therapy.
“In recent years there has been a growing appreciation by regulatory authorities that cannabis-based medicines can play a useful role in disease therapy. “The pharmacological treatment for autism spectrum disorders is often poorly tolerated and has traditionally targeted associated conditions, with limited benefit for the core social deficits.
“The pharmacological treatment for autism spectrum disorders is often poorly tolerated and has traditionally targeted associated conditions, with limited benefit for the core social deficits. “Mutations in SYNGAP1 are associated with developmental delay, epilepsy, and autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Epilepsy is often drug-resistant in this syndrome with frequent drop attacks.
“Mutations in SYNGAP1 are associated with developmental delay, epilepsy, and autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Epilepsy is often drug-resistant in this syndrome with frequent drop attacks.