 “Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction, associated with the presence of restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities. Cannabis has been used to alleviate symptoms associated with ASD.
“Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction, associated with the presence of restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities. Cannabis has been used to alleviate symptoms associated with ASD.
Method: We carried out a systematic review of studies that investigated the clinical effects of cannabis and cannabinoid use on ASD, according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA checklist). The search was carried out in four databases: MEDLINE/PubMed, Scientific Electronic Library Online (SciELO), Scopus, and Web of Science. No limits were established for language during the selection process. Nine studies were selected and analyzed.
Results: Some studies showed that cannabis products reduced the number and/or intensity of different symptoms, including hyperactivity, attacks of self-mutilation and anger, sleep problems, anxiety, restlessness, psychomotor agitation, irritability, aggressiveness perseverance, and depression. Moreover, they found an improvement in cognition, sensory sensitivity, attention, social interaction, and language. The most common adverse effects were sleep disorders, restlessness, nervousness and change in appetite.
Conclusion: Cannabis and cannabinoids may have promising effects in the treatment of symptoms related to ASD, and can be used as a therapeutic alternative in the relief of those symptoms. However, randomized, blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials are necessary to clarify findings on the effects of cannabis and its cannabinoids in individuals with ASD.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34043900/
“Cannabis and cannabinoids have very promising effects in the treatment of autistic symptoms and can be used in the future as an important therapeutic alternative to relieve those symptoms, especially bouts of self-mutilation and anger, hyperactivity, sleep problems, anxiety, restlessness, psychomotor agitation, irritability, and aggressiveness; as well as improve sensory sensitivity, cognition, attention, social interaction, language, perseverance, and depression.”
https://www.scielo.br/j/trends/a/LBmJK6d8bqr5jVK6fp3CHXt/?lang=en


 “Central pain after stroke due to brainstem infarction is very rare. Treatment is difficult and specific guidelines are lacking. This is the report of a 61-year-old female patient who, after a posterolateral left medulla oblongata insult with incomplete Wallenberg syndrome, subsequently developed a burning and tingling pain in the contralateral leg and a burning and shooting pain in the ipsilateral face in trigeminal branches 1 and 2. More than 3 years of therapy with amitriptyline, gabapentin, pregabalin and various grade II and III opioids was ineffective or showed intolerable side effects. The administration of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol as an oromucosal spray in a 1:1 ratio improved the pain situation and quality of life quickly and permanently. The encouraging results in the present case may suggest that treatment with medical cannabis should be considered in similar cases when standard therapies are insufficient.”
“Central pain after stroke due to brainstem infarction is very rare. Treatment is difficult and specific guidelines are lacking. This is the report of a 61-year-old female patient who, after a posterolateral left medulla oblongata insult with incomplete Wallenberg syndrome, subsequently developed a burning and tingling pain in the contralateral leg and a burning and shooting pain in the ipsilateral face in trigeminal branches 1 and 2. More than 3 years of therapy with amitriptyline, gabapentin, pregabalin and various grade II and III opioids was ineffective or showed intolerable side effects. The administration of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol as an oromucosal spray in a 1:1 ratio improved the pain situation and quality of life quickly and permanently. The encouraging results in the present case may suggest that treatment with medical cannabis should be considered in similar cases when standard therapies are insufficient.” “Melanoma is one of the most aggressive malignances in human. Recently developed therapies improved overall survival rate, however, the treatment of melanoma still remains a challenging issue.
“Melanoma is one of the most aggressive malignances in human. Recently developed therapies improved overall survival rate, however, the treatment of melanoma still remains a challenging issue. 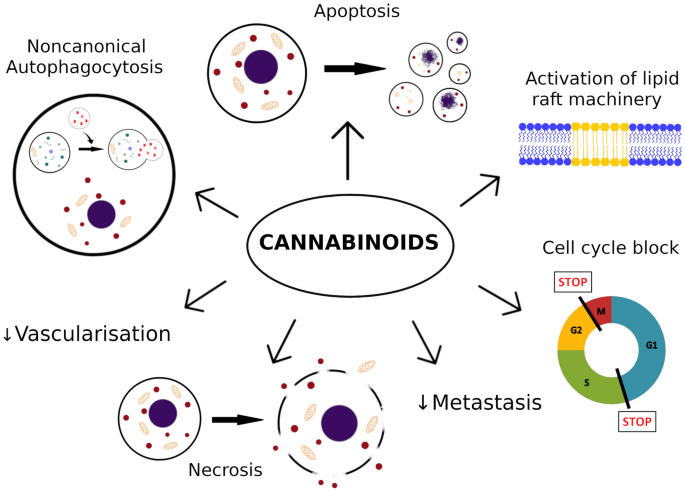
 “The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a composite cell-signaling system that allows endogenous cannabinoid ligands to control cell functions through the interaction with cannabinoid receptors. Modifications of the ECS might contribute to the pathogenesis of different diseases, including cancers. However, the use of these compounds as antitumor agents remains debatable.
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a composite cell-signaling system that allows endogenous cannabinoid ligands to control cell functions through the interaction with cannabinoid receptors. Modifications of the ECS might contribute to the pathogenesis of different diseases, including cancers. However, the use of these compounds as antitumor agents remains debatable. 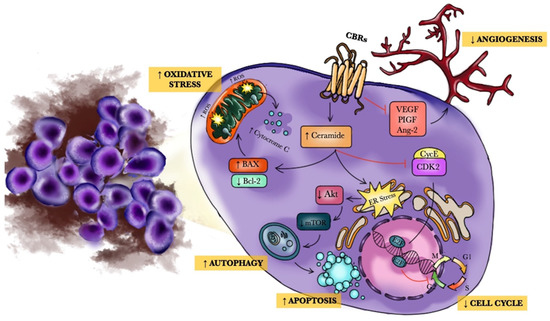
 “Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and antiretroviral therapy can independently induce HIV-associated neuropathic pain (HIV-NP).
“Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and antiretroviral therapy can independently induce HIV-associated neuropathic pain (HIV-NP). “Background:
“Background:  “Introduction:
“Introduction: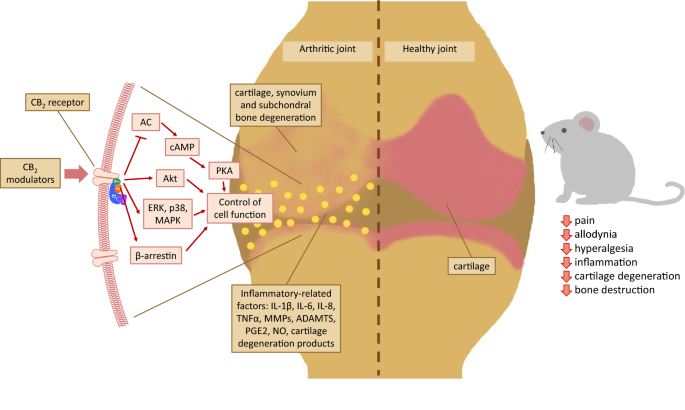 “Over the last several decades, the percentage of patients suffering from different forms of arthritis has increased due to the ageing population and the increasing risk of civilization diseases, e.g. obesity, which contributes to arthritis development. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are estimated to affect 50-60% of people over 65 years old and cause serious health and economic problems. Currently, therapeutic strategies are limited and focus mainly on pain attenuation and maintaining joint functionality. First-line therapies are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; in more advanced stages, stronger analgesics, such as opioids, are required, and in the most severe cases, joint arthroplasty is the only option to ensure joint mobility.
“Over the last several decades, the percentage of patients suffering from different forms of arthritis has increased due to the ageing population and the increasing risk of civilization diseases, e.g. obesity, which contributes to arthritis development. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are estimated to affect 50-60% of people over 65 years old and cause serious health and economic problems. Currently, therapeutic strategies are limited and focus mainly on pain attenuation and maintaining joint functionality. First-line therapies are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; in more advanced stages, stronger analgesics, such as opioids, are required, and in the most severe cases, joint arthroplasty is the only option to ensure joint mobility.